Connecting Jira Service Management (JSM) with Jira Software helps organizations combine IT service management with DevOps, quality assurance, and project management workflows. But most organizations hit a wall: how do you keep data synchronized between instances when teams work across different departments, time zones, or separate companies?
This is where your integration architecture actually matters. While native Atlassian tools and generic iPaaS platforms handle basic connectivity, they struggle with cross-company collaboration, multi-instance synchronization, and granular control requirements.
This guide covers everything from understanding the fundamental differences between JSM and Jira Software to implementing enterprise-grade integration with flexible scripting control and AI-assisted configuration.
Note: Jira now refers to “issues” as “work items” throughout the platform. This guide uses the updated terminology.
Key Takeaways
- JSM handles IT service management (incidents, service requests, SLAs, customer portals) while Jira Software focuses on development workflows (sprints, backlogs, releases), and integration bridges these distinct functions.
- Native Atlassian tools work for simple same-site scenarios, but cross-company collaboration and multi-instance networks require purpose-built integration solutions with independent control for each side.
- Exalate provides AI-assisted configuration through Aida for quick setup, plus full Groovy scripting for complex sync scenarios, including conditional field mapping and workflow transformations.
- Integration eliminates manual data entry between systems, accelerates incident resolution, and gives managers complete visibility across IT service and development workflows.
- The right integration tool should offer bidirectional sync, custom field transformation, predictable pricing, and the ability to scale from two instances to complex multi-tenant networks.

What Makes Jira Service Management Jira Software Integration Challenging?
Most teams underestimate the complexity here. The challenge is maintaining data integrity, security, and control as your integration needs evolve.
Cross-Company Data Security and Control
When integrating with external vendors, managed service providers, or clients, you need complete control over what data leaves your organization.
Some integration tools create a central point where sensitive information passes through third-party infrastructure. This introduces security risks and compliance concerns, especially for organizations in regulated industries like healthcare, finance, or government.
With independent integration control, each organization maintains full authority over its data. You decide what gets synchronized outward and what gets accepted inward, without relying on a central hub that could become compromised or create vendor lock-in.
Multi-Instance Integration Complexity
Organizations often need more than simple two-instance integration. You might have separate JSM portals for HR, IT, facilities, and customer support, plus multiple Jira Software instances for different development teams, regional offices, or business units.
Traditional hub-and-spoke integration tools struggle here. They force you into rigid models where all data flows through a central hub, creating a single point of failure.
If the hub experiences issues, all your integrations stop working. As you add more instances, the hub becomes increasingly complex to manage and more vulnerable to performance bottlenecks.
An integration that scales to form a multi-instance network eliminates this problem. Each connection operates independently, so a failure in one integration doesn’t affect others. You can scale from 2 instances to 20+ instances without exponentially increasing complexity or risk.
Custom Field Mapping and Transformation Requirements
JSM and Jira Software handle fields differently. Request types, SLAs, approvals, customer portals, and satisfaction ratings in JSM don’t have direct equivalents in Jira Software. Meanwhile, Jira Software’s sprint fields, story points, and release tracking don’t exist in JSM.
Generic integration platforms offer pre-built field mappings that work for basic scenarios, but they fail when you need custom transformations, conditional logic, or bidirectional synchronization with different field structures on each side.
You might need to transform a JSM request type into a Jira Software work item type based on specific conditions, or sync comments bidirectionally while filtering out internal notes.
This requires flexible, scriptable integration logic that most no-code tools cannot provide.
Why Native Atlassian Integration Tools Fall Short for Ongoing Integration
Atlassian provides native options like Jira Cloud Migration Assistant and Copy Product Data for moving work between instances. These tools are designed for one-time migrations, not continuous, real-time synchronization.
They lack bidirectional sync capabilities, custom field mapping flexibility, and conditional logic required for ongoing collaboration scenarios.
You cannot use them to maintain synchronized data between a development team’s Jira Software instance and a support team’s JSM instance where both sides are actively updating information.
Native automation within JSM works well for simple linking and status updates when both products are on the same Atlassian site. But for cross-instance, cross-company, or complex transformation scenarios, you need a purpose-built integration solution.
How Does Jira Software Differ from Jira Service Management?
Although both are Atlassian Jira products, Jira Service Management and Software serve different purposes and audiences.
Jira Service Management
JSM provides templates and functionality for IT service management, HR service delivery, and facility management. Your organization can report and resolve all ITSM incidents faster using automated tracking and approval workflows.
Core JSM capabilities include:
- Customer-facing portals for service requests
- SLA tracking and management
- Incident and problem management
- Change management with automated risk assessments
- Asset and configuration management (Premium/Enterprise)
- Knowledge base integration
- Queue management and agent workflows
Jira Software
Jira Software caters to all activities in the development pipeline, from mapping work items to tracking releases and dependencies.
Core Jira Software capabilities include:
- Agile boards (Scrum and Kanban)
- Sprint planning and backlog management
- Timeline views and dependency tracking
- DevOps integration with CI/CD tools
- Code repository connections
- Release management
- Development-focused reports and insights
The fundamental difference: JSM optimizes for customer-facing service delivery and ITIL processes, while Jira Software optimizes for development team productivity and agile workflows.
Why Integrate Jira Service Management and Jira Software
Development and Support Team Alignment
Software development teams use Jira Software to track feature development, bug fixes, and technical debt. IT support teams use JSM to manage customer incidents, service requests, and internal tickets.
Without integration, when a customer reports a critical bug through the service desk, someone must manually create a corresponding development ticket in Jira Software. As developers work on the fix, support teams have no visibility into progress. They must repeatedly ask for updates, and customers receive inconsistent information about resolution timelines.
With integration, customer-reported incidents automatically create development tickets. As developers update status, add comments, or change priorities, support teams and customers see real-time progress. When the fix is deployed, the service desk ticket automatically closes with resolution notes.
Cross-Company Collaboration Scenarios
Many organizations need to integrate JSM and Jira Software instances across company boundaries:
- Managed service providers handling IT operations
- Vendors developing custom software
- Outsourcing partners providing specialized services
- Clients needing visibility into project progress
Cross-company integration requires careful consideration of data security, access controls, and governance. Each organization needs complete control over what information flows outward and what gets accepted inward.
Multi-Instance Portal Consolidation
Organizations with complex IT service structures often require employees to access multiple JSM instances for different support functions. This creates a fragmented user experience where people must remember which portal to use for which type of request.
For example, restaurant managers may need to submit HR and payroll tickets through the corporate group JSM portal, raise operational technology issues with a specialized support team’s JSM instance, and request IT assistance from an external vendor’s JSM portal. Each portal has different login credentials, workflows, and interfaces.
Integration enables a unified view where employees access a single interface while their requests get routed to the appropriate backend system. Each JSM instance maintains independent ticket management and workflows, but users experience seamless, consolidated service delivery.
Jira Service Management to Jira Software Integration Use Cases
Use Case 1: Customer-Reported Bug Escalation
Challenge: Support teams receive customer bug reports through JSM, but developers work in Jira Software. Without integration, support agents manually copy bug details to development tickets, losing context and delaying resolution. Customers don’t receive updates until agents manually check developer progress.
Solution: Bidirectional integration automatically creates linked work items in Jira Software when support agents categorize JSM tickets as bugs. Developer comments and status changes sync back to JSM in real-time, giving support agents instant visibility into fix progress.
Real-World Application: A SaaS company reduced average bug resolution time from 5 days to 2 days after implementing automated escalation. Support agents stopped spending 2+ hours daily copying ticket information between systems, and customer satisfaction scores improved when customers received automatic updates on bug fix progress.
Use Case 2: Feature Request Pipeline Management
Challenge: Customer feature requests arrive through JSM portals, but product and development teams prioritize work in Jira Software. Without integration, product managers manually review JSM requests and create corresponding Jira Software stories, leading to duplicates and lost requests.
Solution: Integration syncs feature requests from JSM to a dedicated Jira Software backlog. Product managers prioritize in Jira Software, and their decisions sync back to JSM, automatically updating customers on request status. Duplicate detection prevents the same request from creating multiple development items.
Real-World Application: A B2B software company connected three regional JSM portals to a central Jira Software instance for product development. Feature requests from customers worldwide now flow into a single prioritized backlog, while each regional support team maintains visibility into their customers’ specific requests.
Use Case 3: MSP Multi-Tenant Service Delivery
Challenge: A managed service provider supports 50+ clients, each with their own Jira Software or JSM instance. The MSP needs to receive work items from client systems, work on them internally, and push updates back—without exposing client data to other clients or requiring access to client admin credentials.
Solution: Independent integration connections link each client instance to the MSP’s internal JSM. Each connection has its own sync rules, ensuring Client A’s data never mixes with Client B’s. The MSP controls their side; clients control their side. No shared admin access required.
Real-World Application: An IT services firm managing infrastructure for healthcare organizations established compliant integrations that sync incident tickets while automatically filtering out PHI (protected health information) from crossing organizational boundaries. Each healthcare client’s compliance team approved only the specific fields that could sync to the MSP.
Use Case 4: DevOps Incident Response Coordination
Challenge: Site reliability engineers detect production issues through monitoring tools that create Jira Software work items. Customer-facing impact needs to be communicated through JSM, but there’s no automatic connection between the development incident and the customer communication.
Solution: Integration links development incidents in Jira Software to customer-facing incident records in JSM. When SRE teams update the technical incident with root cause analysis or fix timelines, that information syncs to JSM for customer communication. When the development incident resolves, JSM tickets close automatically with resolution notes.
Real-World Application: An e-commerce platform integrated its engineering incident management in Jira Software with customer support in JSM. During a payment processing outage, the integration automatically created a customer incident, synced real-time updates from the engineering team, and closed 200+ customer tickets simultaneously when the fix was deployed.
Use Case 5: Enterprise Change Management Coordination
Challenge: IT change management processes in JSM require development team input for technical changes. Developers submit change requests through Jira Software, but change advisory boards work in JSM. Manual coordination leads to missed approvals and failed changes.
Solution: Integration syncs change requests between development workflows in Jira Software and formal change management processes in JSM. Technical details flow to the CAB for review, and approval decisions sync back to development systems. Developers receive automated notifications when their changes are approved or require additional information.
Real-World Application: A financial services firm integrated development release management with IT change control. Code releases now automatically trigger change requests in JSM, reducing the change failure rate from 15% to 3% by ensuring all releases go through proper review before deployment.
Use Case 6: Vendor Software Development Coordination
Challenge: An organization outsources software development to an external vendor. The vendor works in their own Jira Software instance, but the organization’s internal teams need visibility into development progress through their JSM instance. Neither organization wants to give the other admin access to their systems.
Solution: Integration connects the two instances while maintaining complete independence. Each organization controls what data leaves their system and what data they accept. The vendor shares only relevant development updates; the client shares only approved requirements and feedback.
Real-World Application: A retail company working with an offshore development partner established integration that syncs user story status and developer comments without exposing internal cost estimates, resource allocation, or competitive information from either side.
Use Case 7: Merger and Acquisition System Consolidation
Challenge: After acquiring another company, organizations often run parallel Jira systems for months or years. Teams need to collaborate across legacy systems while maintaining separate administrative control during the transition period.
Solution: Integration enables cross-system collaboration without forcing immediate migration. Teams in the acquiring company’s Jira Software can work with teams in the acquired company’s JSM instance. As systems consolidate over time, integration rules adjust without disrupting ongoing work.
Real-World Application: A technology company completing an acquisition used integration to connect the acquired company’s JSM with their own Jira Software for 18 months during system consolidation. Development teams collaborated on shared projects without either company’s IT team losing control of their respective systems.
What Are the Key Benefits of JSM-Jira Software Integration
Breaking Down Information Silos
Integration ensures all team members and stakeholders have access to project-relevant data when needed. Developers see customer impact and business priority. Support teams see technical complexity and development progress. Managers see complete workflow visibility across departments.
Information silos create hidden knowledge gaps where critical context gets lost. Integration makes implicit knowledge explicit and accessible.
Accelerating Incident Resolution Time
Faster incident resolution leads to improved customer satisfaction and reduced business impact. Integration eliminates manual handoffs, reduces context-switching, and ensures the right information reaches the right team immediately.
When critical issues arise, integrated systems automatically escalate to development teams with complete context. No one wastes time gathering information or waiting for email responses. Resolution starts immediately.
Reducing Manual Data Entry
Manual data entry between systems consumes hours of productive time and introduces transcription errors. Someone updates a ticket in one system, then must remember to update the corresponding ticket elsewhere. Fields get missed. Details get truncated. Information drifts out of sync.
Integration automates this completely. Changes propagate automatically with perfect accuracy. Teams spend time solving problems instead of maintaining duplicate records.
Improving Resource Allocation and Planning
When development and support data synchronize, managers gain complete visibility into team capacity, workload distribution, and bottlenecks. They can make data-driven decisions about resource allocation, hiring needs, and process improvements.
Without integration, each team operates as an isolated island. With integration, you see the complete workflow from customer request through development and deployment.
Features to Consider When Choosing a JSM-Jira Software Integration Tool
Before selecting an integration tool, document your specific requirements. Consider whether you’re integrating within a single organization or across company boundaries. Evaluate whether you need simple field synchronization or complex conditional logic and data transformations.
Ease of Use: AI-Assisted Configuration and Scripting Options
Full Scripting Capabilities enable handling any integration complexity. You can implement conditional synchronization, custom field transformations, complex business logic, multi-step workflows, and integration with external APIs.
AI-Assisted Configuration provides scripting flexibility with significantly reduced complexity. Tools like Exalate’s Aida allow you to describe integration requirements in plain language and automatically generate the corresponding Groovy script code. This makes advanced configurations accessible to users without extensive coding experience.
Choose a tool that matches your team’s technical capabilities while providing a growth path to handle future complexity.
Security and Compliance Standards
For integrations handling sensitive customer data and proprietary development information, security isn’t optional. Evaluate:
- Compliance Certifications: ISO 27001 and other relevant certifications demonstrate adherence to international security standards. Exalate maintains ISO 27001:2022 certification.
- Encryption Standards: Data protection requires encryption at multiple levels—TLS protocols protect data during synchronization (in transit), and encrypted storage ensures data remains protected when not actively syncing (at rest).
- Role-Based Access Control: Define exactly who can configure, modify, or view integration settings. This prevents unauthorized changes to sync rules and protects sensitive field mappings.
For detailed security documentation and compliance certifications, visit the Exalate Trust Center.
Affordability and Total Cost of Ownership
Integration tool costs vary significantly based on pricing models, included features, and hidden expenses.
Consider the complete total cost of ownership: initial setup costs, monthly or annual subscription fees, costs per user or per instance, implementation services if needed, ongoing maintenance and support, and costs to scale as you add instances or users.
Some platforms charge per transaction, creating unpredictable costs as your integration usage grows. Others charge per user, which can become expensive for large organizations.

Calculate time and money savings from automated bidirectional sync.
Ability to Scale
Evaluate how the integration tool handles scaling:
- Can you add new instances without exponentially increasing complexity?
- Does performance degrade as you add connections?
- Can you modify existing integrations without breaking others?
- Does the pricing model remain affordable as you scale?
Independent architecture scales more efficiently than centralized hubs because each connection operates independently. Adding the tenth connection is no more complex than adding the second.
Bidirectional Sync and Conflict Resolution
True bidirectional synchronization means changes in either system propagate to the other. But what happens when both systems change the same field simultaneously?
Evaluate how the tool handles sync conflicts, whether it supports different sync strategies for different fields, and whether you can define priority rules when conflicts occur.
Custom Field Support and Transformation
JSM and Jira Software use different field structures, and most organizations add extensive custom fields. Evaluate:
- Can you map custom fields by ID or display name?
- Can you transform values between different field types?
- Can you implement conditional logic based on custom field values?
- Can you handle complex field types like cascading select, multi-select, and user pickers?
Support and Documentation Quality
Integration issues need rapid resolution because they block critical workflows. Evaluate response time commitments, availability of technical experts, documentation quality and completeness, community forums and knowledge bases, and whether implementation assistance is available.
JSM-Jira Software Integration Tools: Native and Third-Party Options
Native Atlassian Options
- Jira Automation (Same Site): For JSM and Jira Software on the same Atlassian Cloud site, native automation rules can create, link, and update work items across projects. This works well for simple linking scenarios but lacks cross-instance capability and advanced transformation logic.
- Atlassian Assist (Slack Integration): Provides conversational ticketing through Slack, connecting to JSM. Useful for simple request intake but not designed for system-to-system integration.
- API and Forge Apps: Atlassian’s REST APIs and Forge platform enable custom integrations. This requires development resources and ongoing maintenance but offers complete flexibility for organizations with in-house development capabilities.
Third-Party Integration Platforms
Exalate
- Purpose-built for work management system integration with an independent peer-to-peer architecture.
- Supports Jira, JSM, ServiceNow, Azure DevOps, Salesforce, Zendesk, Freshservice, Freshdesk, GitHub, and Asana.
- Offers AI-assisted configuration through Aida plus full Groovy scripting for complex scenarios.
- ISO 27001:2022 certified.

Zapier
- General-purpose automation platform with broad app connectivity.
- Works well for simple trigger-action workflows but lacks deep bidirectional sync capabilities and advanced field transformation for complex Jira scenarios.
Workato
- Enterprise iPaaS platform with extensive integration capabilities.
- Powerful for organizations already invested in the platform but can be complex and expensive for straightforward JSM-Jira Software integration needs.
Make (formerly Integromat)
- Visual automation platform with good Jira connectivity.
- Suitable for straightforward automation scenarios but may require workarounds for complex bidirectional sync requirements.
Unito
- Focused on two-way sync between project management tools.
- Good for basic field mapping but may lack flexibility for complex conditional logic and cross-company scenarios.
Getint
- Jira-focused integration tool with support for various platforms.
- Offers both simple and advanced configuration options.
Choosing the Right Tool
Choose native automation when:
- Both products are on the same Atlassian site
- You need simple linking and status synchronization
- Your requirements won’t grow beyond basic automation
Choose Exalate when:
- You need cross-instance or cross-company integration
- Complex field transformations and conditional logic are required
- Security and independent control are priorities
- You’re building a multi-instance integration network
- You want AI-assisted configuration with scripting flexibility
Why Exalate Excels for JSM-Jira Software Integration
Exalate meets enterprise integration criteria while providing unique advantages specifically for JSM-Jira Software scenarios:
- Flexible Configuration with Aida: Handle any integration complexity using Groovy scripts, with AI-assisted configuration that generates code from natural language descriptions. Describe what you want, review the generated script, and refine as needed.
- Bidirectional Sync: Changes propagate in both directions with full conflict resolution capabilities. Define exactly how each field behaves when updated from either side.
- Support for All Deployment Models: Works with Jira Cloud and hybrid combinations. Supports connections between cloud instances and instances behind firewalls.
- Custom Field Mastery: Sync any field type, including custom fields unique to your organization. Transform values, implement conditional logic, and handle complex field types.
- Security and Compliance: ISO 27001 certified with role-based access control, encryption of data in transit and at rest, and data residency controls. Full details available at the Exalate Trust Center.
- Multi-Platform Support: Beyond JSM and Jira Software, Exalate connects with ServiceNow, Azure DevOps, Azure DevOps Server, Salesforce, Zendesk, Freshservice, Freshdesk, GitHub, and Asana. Build integration networks that span your entire technology ecosystem.
- ROI Impact: Organizations typically see measurable time savings within the first month. Calculate your potential ROI based on your specific integration scenario.

Calculate time and money savings from automated bidirectional sync.
Aida: Making Advanced Integration Accessible
The Challenge of Custom Field Mapping
JSM and Jira Software use different field structures, and most organizations add extensive custom fields to match their specific workflows. Mapping these fields correctly requires understanding both systems’ data structures and writing code to handle transformations.
Traditional integration tools offer two options: use pre-built field mappings that work for standard fields only, or hire developers to write custom code. Neither option is ideal for most organizations.
How Aida Transforms Integration Configuration
Exalate’s Aida (AI-assisted integration) bridges the gap between no-code simplicity and full scripting power. Instead of writing Groovy code from scratch, you describe what you want in plain language, and Aida generates the appropriate script.
Aida understands:
- Field types and data structures in both JSM and Jira Software
- Common transformation patterns and business logic
- Exalate’s scripting API and syntax
- Your existing configuration and integration context
Practical Aida Examples
Custom Field Synchronization
Your description: “Sync the Customer Impact field from JSM to a custom field called Business Priority in Jira Software.”
Aida-generated script:
// Outgoing (JSM side):
replica.customFields."Customer Impact" = issue.customFields."Customer Impact"
// Incoming (Jira Software side):
issue.customFields."Business Priority".value = replica.customFields."Customer Impact"?.valueCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Conditional Status Mapping
Your description: “When JSM status changes to ‘Resolved’, set Jira Software status to ‘Done’. When JSM status is ‘In Progress’, set Jira Software status to ‘In Development’.”
Aida-generated script:
// Incoming (Jira Software side):
if (replica.status.name == "Resolved") {
issue.setStatus("Done")
} else if (replica.status.name == "In Progress") {
issue.setStatus("In Development")
}Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Filtering Comments
Your description: “Sync comments from JSM to Jira Software, but don’t sync any comments that contain the word ‘internal’.”
Aida-generated script:
// Incoming (Jira Software side):
replica.comments.each { comment ->
if (!comment.body.toLowerCase().contains("internal")) {
issue.comments << comment
}
}Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The Iterative Refinement Process
Aida supports iterative refinement. Describe your requirements, review the generated script with highlighted additions and modifications, test in your environment, refine your description if results aren’t exactly right, and publish when everything works correctly.
You don’t need to get the description perfect on the first try. Progressively refine until the integration behaves exactly as needed.
When to Use Aida vs. Manual Scripting
Use Aida for:
- Standard field mappings with variations
- Common transformation patterns
- Conditional logic based on field values
- Comment and attachment synchronization
- Getting started with new integrations quickly
Consider manual scripting for:
- Highly complex business logic spanning multiple systems
- Integration with external APIs beyond Jira
- Performance-critical operations requiring optimization
- Unique transformation requirements
Even for complex scenarios, Aida provides a strong starting point that you can manually refine.
Getting Started With JSM-Jira Software Integration
Implementation Timeline
Basic integration setup takes 15-30 minutes using Exalate’s workspace-based configuration and Aida. This includes connecting your JSM and Jira Software instances, establishing the connection, and configuring simple field synchronization.
Advanced configurations with custom field mappings, complex automation triggers, and multi-instance scenarios may require several hours to a few days, depending on your specific requirements and the complexity of your existing workflows.
Planning Your Integration
Before starting:
- Document requirements: What data needs to sync? In which direction? Under what conditions?
- Identify stakeholders: Who from each team needs to provide input on field mappings and workflows?
- Map your fields: Create a spreadsheet showing source fields, destination fields, and any transformation rules.
- Define triggers: What conditions should automatically initiate synchronization?
- Plan testing: How will you verify the integration works correctly before production deployment?
How to Sync Jira Service Management and Jira Software Using Exalate
- Go to the integrations page and find your Jira connector. Sign in to your Exalate console using your personal credentials. Google sign-in is also available.

- Establish a connection between Jira instances. Give them a descriptive name and pass the authentication process.
- Configure the connection. Use Exalate’s Groovy scripting engine to write rules that will control and define how both Jira instances will interact and share data.
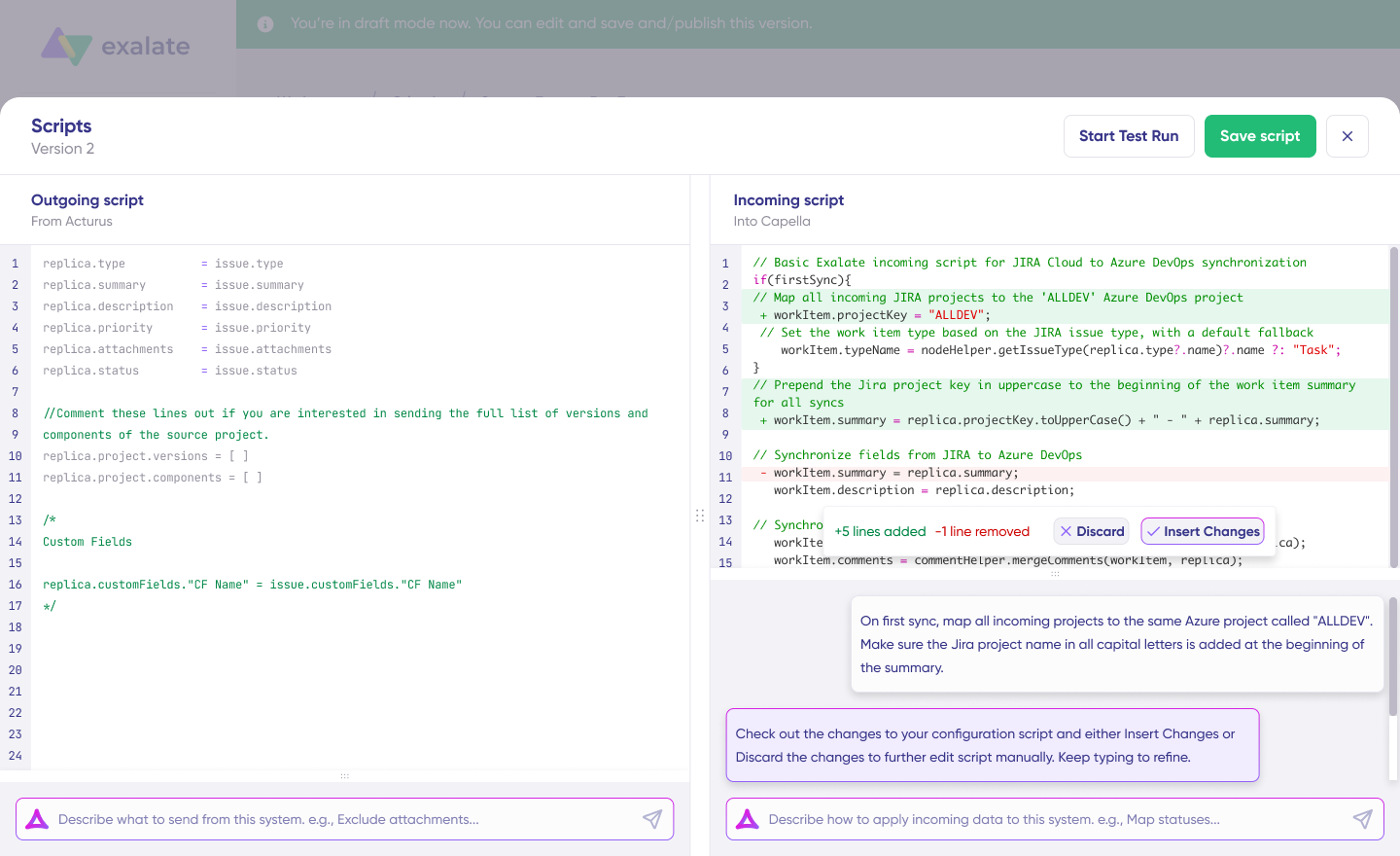
- Generate scripts using Aida. Get the best out of Exalate’s scripting engine by using the AI-powered assistant to generate scripts according to user input and text-based prompts.
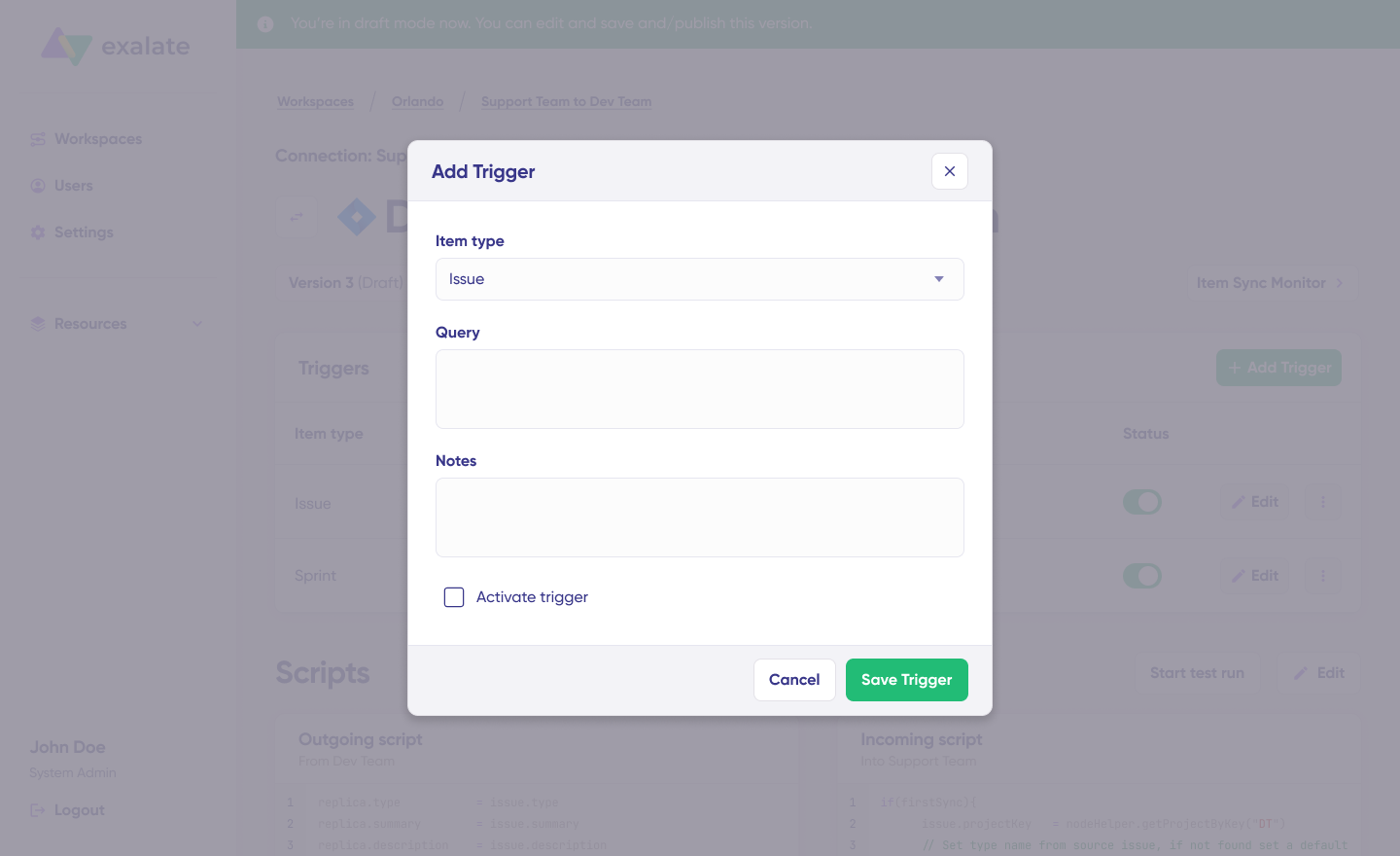
- Set up triggers. Create automated triggers using JQL to determine how the Jira instances will handle the integration rules.
- Start syncing your tasks. You can initiate multiple Jira syncs directly from the Exalate console or from the Exalate panel within the Jira work.
For a detailed breakdown of every step of integrating multiple Jira instances, read this comprehensive guide.
Next Steps
Ready to integrate your Jira instances with complete control, enterprise-grade security, and unlimited customization?
Book a demo with Exalate’s integration engineers to discuss your specific requirements and see how independent architecture solves challenges that centralized platforms cannot address. The team will help you design an integration strategy that scales from your initial two-instance setup to complex multi-tenant networks as your needs evolve.

Frequently Asked Questions
How does Exalate work with Jira Service Management and Jira Software?
Exalate connects JSM and Jira Software using a script-based approach where each side has its own configuration. Each side communicates through sync rules you control independently. Think of it like having two translators—one on each side—who know exactly what information to share and how to format it for the other platform. Neither side depends on the other’s configuration, and changes on one side don’t affect the partner’s setup.
What types of data can be synchronized between JSM and Jira Software?
You can synchronize virtually any data type: work item summaries, descriptions, priorities, statuses, assignees, reporters, custom fields, attachments, comments, labels, components, fix versions, time tracking, SLAs, organizations, request types, approvals, and customer portal interactions. You control exactly what synchronizes using customizable sync rules. Check out all the entities available for sync.
Does Exalate support automation for JSM-Jira Software integration?
Yes, platform-native triggers use JQL queries to automatically initiate synchronization when specific conditions are met. Aida (AI-assisted configuration) allows you to implement complex conditional logic, field transformations, and workflow automation using natural language descriptions that convert into working scripts. You can automate field mappings, escalate high-priority JSM requests to Jira Software as critical bugs, route specific work types to designated teams based on custom field values, and trigger external webhooks during synchronization.
Can Exalate sync work items between different Jira instances?
Absolutely. Exalate specializes in multi-instance synchronization across separate Jira Cloud instances, and hybrid combinations of Cloud and on-premise environments. This works across different organizations, business units, departments, or external partners. You can integrate your internal JSM instance with a vendor’s Jira Software Cloud, synchronize across regional setups, or connect subsidiary Jira instances back to corporate systems.
Can I integrate more than two Jira instances simultaneously?
Yes. Exalate supports extensive multi-instance networks—three, four, five, or twenty-plus JSM and Jira Software instances simultaneously. Each connection maintains independent sync rules and configurations, operating as a separate integration that doesn’t affect others. This scalability makes Exalate ideal for organizations with complex IT service structures, multiple business units, or extensive partner networks requiring coordinated but independent integration connections.
What is the difference between Jira Software and Jira Service Management?
Jira Software focuses on software development workflows—sprint planning, backlog management, code repository integration, and release tracking. Jira Service Management focuses on IT service management—customer portals, incident management, SLA tracking, change management, and asset management. Both are built on the Jira platform but serve different user needs. Integration connects these distinct functions so development and service teams can collaborate effectively.
Do I need coding knowledge to use Exalate?
Not necessarily. Exalate’s Aida (AI-assisted configuration) lets you describe integration requirements in plain language, like “sync priority field but map High to Urgent,” and generates the corresponding Groovy script. You review the generated code, test it, and refine your description if needed. This makes advanced configurations accessible to non-developers while still providing full scripting power for complex scenarios when needed.
Does Exalate sync custom fields between JSM and Jira Software?
Yes, custom fields are fully supported with complete flexibility. You can map custom fields using their IDs or display names, transform values between different field types, implement conditional logic based on custom field values, synchronize custom fields bidirectionally with different structures on each side, and handle complex custom field types like cascading select, multi-select, and user pickers.
Is Exalate secure for sensitive data?
Exalate uses encrypted connections (TLS/HTTPS) and doesn’t store your data on third-party servers since the architecture uses direct peer-to-peer connections. Exalate maintains ISO 27001:2022 certification with role-based access control and encryption of data both in transit and at rest. You can implement field-level filtering in your sync rules to exclude sensitive information or mask certain values. Visit the Trust Center for detailed security documentation.
How does Exalate compare to Zapier or Workato for Jira integration?
Exalate differs fundamentally from general-purpose iPaaS platforms. While Zapier and Workato offer broad connectivity across thousands of applications with pre-built actions, Exalate specializes in deep, bidirectional synchronization between work management and ITSM tools. General iPaaS platforms typically offer limited customization—basic field mapping and simple conditional logic. Exalate provides unlimited customization through full scripting capabilities. For organizations needing sophisticated Jira integration with granular control, Exalate’s specialized architecture and deep platform integration deliver capabilities that general-purpose tools cannot match.
What platforms does Exalate support besides JSM and Jira Software?
Exalate connects with ServiceNow, Azure DevOps, Azure DevOps Server, Salesforce, Zendesk, Freshservice, Freshdesk, GitHub, Asana, and supports custom connectors for additional platforms. This allows you to build integration networks that span your entire technology ecosystem.
Can Exalate sync JSM request types to Jira Software work item types?
Yes. You can map JSM request types to specific Jira Software work item types using conditional logic. For example, JSM “Bug Report” requests can automatically create “Bug” work items in Jira Software, while “Feature Request” requests create “Story” work items. The mapping can be as simple or complex as your workflow requires.
How does Exalate handle different workflows in JSM and Jira Software?
Exalate supports workflow status mapping between systems. You define how statuses in one system correspond to statuses in the other. When a work item transitions in JSM, the corresponding Jira Software work item can automatically transition to the mapped status. You can implement conditional logic for complex workflow scenarios where mappings aren’t one-to-one.
Does Exalate work with Jira assets and configuration items?
Exalate can synchronize asset and configuration item data when included in JSM work items. For dedicated asset synchronization needs, contact Exalate’s team to discuss your specific requirements.
Can I test my integration before going live?
Yes. Exalate’s Test Run feature allows you to validate configurations before production deployment. Run test synchronizations to verify field mappings work correctly, check that conditional logic behaves as expected, and confirm workflow transitions map properly, all before affecting production data.
Recommended Reads:
- Multiple Jira Instances: How to Connect For Efficient Collaboration
- Jira to Jira Sync: How to Synchronize Multiple Jira Instances in 9 Steps – Idalko
- Advanced integration use cases
- Jira to Jira integration: The Comprehensive Guide
- Jira Integrations: The Guide to Integrating Jira & Other Systems
- How to Implement Jira Issue Sync For Cross-Team Collaboration
- Jira Salesforce Integration: Sync Teams Bidirectionally



