Some organizations work with multiple specialist-managed service providers (MSPs) to lighten the workload burden. IBM might manage cloud infrastructure, AT&T handles network communications, and Cisco provides cybersecurity services.
But this creates a problem: how does your organization unify and integrate with all these MSPs to boost productivity, drive growth, and prevent data loss? That’s where MSP integration comes in.
You need a third-party integration service provider to sync MSPs with your internal systems and connect them with other suppliers.
This article covers MSP integration in detail, what it is, why it matters, the challenges you’ll face, and what to look for in an integration solution.
Key Takeaways
- MSP integration synchronizes your internal systems with managed service providers for real-time data exchange and continuous connectivity during collaboration.
- Integration tools like Exalate, Zapier, and SnapLogic let admins configure syncs, control what data gets shared, and automate workflows.
- Key benefits include creating a unified ecosystem across multiple MSPs, enabling workflow automation, improving flexibility, and boosting ROI through better service quality.
- Common challenges include choosing the right tool for your tech stack, managing costs, preventing security risks, and avoiding vendor lock-in.
- When selecting an integration solution, prioritize bidirectional sync capabilities, AI-assisted configuration, enterprise-grade security, scalability, and flexible field mapping.
- Best practices include using a SIAM approach for multi-MSP management, creating detailed SLAs, and defining clear roles and responsibilities for both internal teams and MSP representatives.

What is MSP Integration?
MSP integration is the process of synchronizing your internal system with managed service providers to obtain data and stay connected throughout your cooperation.
To understand how MSP integration works, let’s first look at how MSPs operate.
Soft Solutions, a software development startup, wants to outsource some of its IT services because they lack the IT team or ITSM (IT service management) model to handle them internally.
They reach out to Fidelity Corp, a customer service MSP that offers managed services on a subscription or per-use basis. Soft Solutions chooses its cooperation model and signs a service-level agreement (SLA) with the MSP.
Second scenario: Soft Solutions also needs to outsource cybersecurity services.
They sign a similar SLA with MyShield, an MSSP (managed security services provider) that ensures their infrastructure stays secure with minimal downtime. Systems are running, customers are happy, and Soft Solutions feels secure.
But there’s a catch. Even though everything works, Soft Solutions struggles to get up-to-date information about system performance. They want to track customer complaints and pain points through key metrics, but can’t get a clear picture across their disconnected systems.
This brings us back to MSP integration. Syncing data with both MyShield and Fidelity Corp would give Soft Solutions better visibility into its operations and market position.
Since both MSPs use separate systems that don’t communicate natively, Soft Solutions needs a third-party integration solution to connect them and enable data sharing.
MSP Integration Solutions
Some MSP integration solutions are native to the MSPs themselves, while others are standalone tools. Every integration service provider relies on APIs and webhooks to connect with other systems. The right choice depends on your technical requirements, MSP relationships, and long-term scalability needs.
Here’s a breakdown of the major options, what they do well, and where they fall short.
Zapier
Zapier lets your team integrate data from multiple MSPs into a unified view. Users automate integrations using “Zaps”, which are pre-built automation workflows that trigger actions based on events in connected apps.
Zapier Pros:
- Quick setup for common app-to-app connections
- No coding required for basic workflows
- Large library of pre-built integrations (6,000+ apps)
- Affordable entry-level pricing for small teams
Zapier Cons:
- Limited customization for complex enterprise scenarios
- One-way sync dominates; bidirectional sync requires workarounds
- Data transformation capabilities are basic
- Not designed for high-volume, real-time ITSM synchronization
- Multi-step Zaps can become expensive at scale
Best for: Small teams needing simple, one-directional data pushes between common business applications. Less suitable for complex MSP ticket synchronization requiring field-level control.
SnapLogic
SnapLogic is an integration platform that uses pre-built connectors called “Snaps” to sync data between applications, databases, and cloud services. With 700+ prebuilt Snaps, it handles connections across enterprise systems, data warehouses, and SaaS applications.
SnapLogic Pros:
- Strong data pipeline capabilities for ETL workloads
- Handles large data volumes efficiently
- Good for batch processing and data migration
- AI-powered suggestions for integration design
- Supports both cloud and on-premise deployments
SnapLogic Cons:
- Steeper learning curve than no-code alternatives
- Requires technical expertise to configure properly
- Pricing can escalate quickly for complex use cases
- Real-time sync capabilities are less mature than batch processing
- Overkill for simple ticket synchronization needs
Best for: Organizations moving large volumes of data between cloud and on-premise environments, particularly for analytics and data warehousing use cases. Better suited for data engineers than service desk admins.
Talend
Talend provides an ETL low-code platform that integrates with any data source or architecture. The platform uses Stitch ETL to extract insights from automated cloud data pipelines, providing a single source of truth for reporting and analytics.
Talend Pros:
- Powerful data transformation and cleansing capabilities
- Open-source option available (Talend Open Studio)
- Strong data quality and governance features
- Good for standardizing data formats across systems
- Comprehensive metadata management
Talend Cons:
- Primarily designed for data integration, not workflow sync
- Complex setup for ITSM-to-ITSM connections
- Real-time synchronization isn’t the primary strength
- Can require significant infrastructure investment
- Learning curve for non-technical users
Best for: Data transformation and cleansing scenarios where you need to standardize information flowing between systems. More appropriate for data teams than IT service management scenarios.
Informatica (Intelligent Cloud Services Data Integration)
Informatica is an ETL-based cloud integration tool for sharing data between clients and MSPs across cloud services. The platform has evolved from traditional data integration into a comprehensive cloud data management suite.
Informatica Pros:
- Massive connector library (50k+ pre-built connectors)
- Enterprise-grade data governance and compliance features
- Strong master data management capabilities
- Specialized tools like Finance 360 and Reference 360
- Robust security and access control
Informatica Cons:
- Enterprise pricing puts it out of reach for smaller organizations
- Complexity requires dedicated integration specialists
- Better suited for data management than real-time ticket sync
- Implementation timelines can extend to months
- Overkill for straightforward MSP integration needs
Best for: Large enterprises with complex data governance requirements connecting to MSPs through cloud services like AWS, Salesforce, Azure, and NetSuite. Less practical for mid-market companies or focused on ITSM synchronization.
Exalate
Exalate is an AI-powered integration solution purpose-built for cross-company and cross-platform work synchronization. Unlike general-purpose iPaaS tools, Exalate focuses specifically on connecting ITSM, DevOps, and CRM platforms for real-time bidirectional sync.
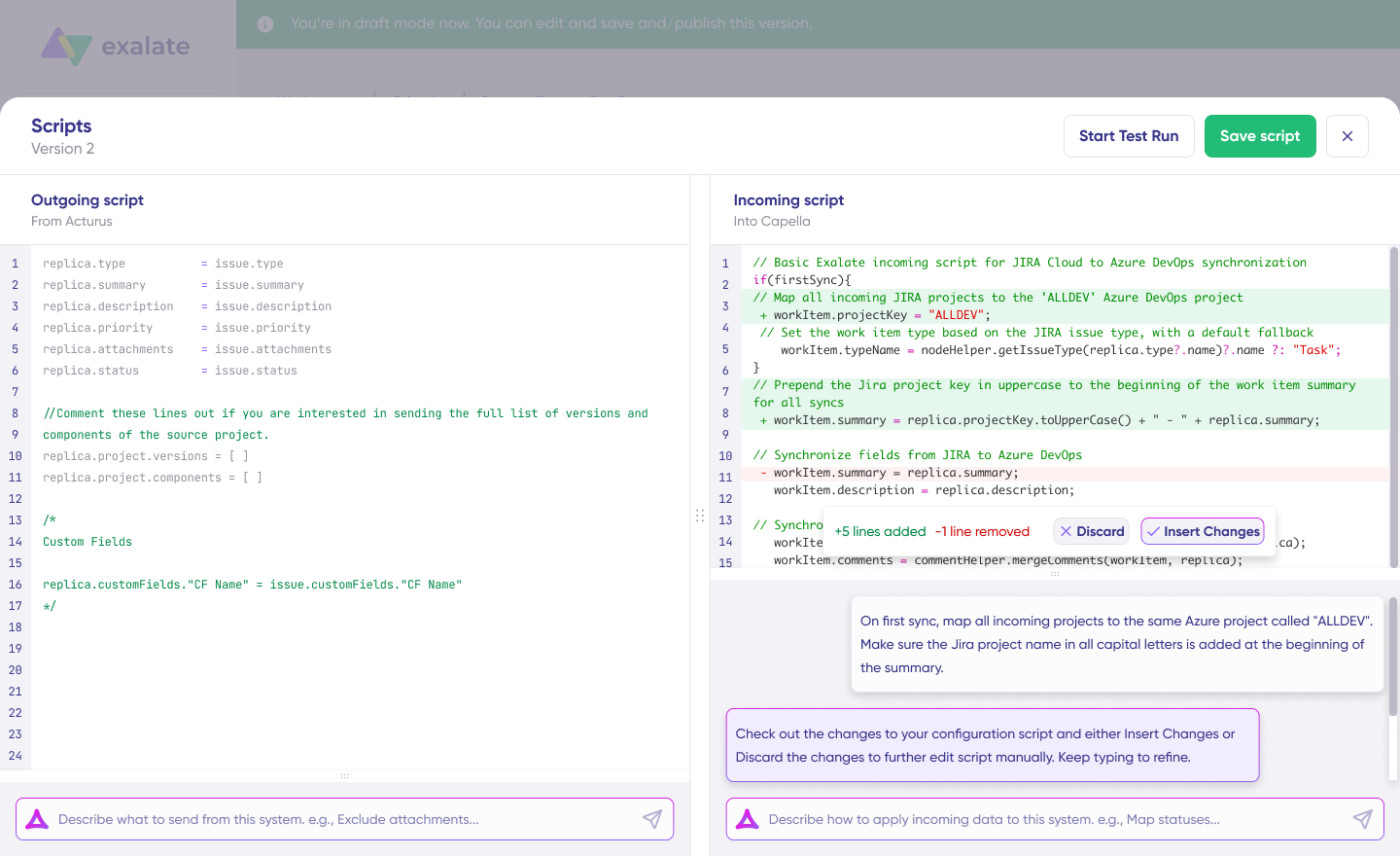
Exalate Pros:
- True bidirectional synchronization with independent control on each side
- AI-assisted configuration through Aida to describe requirements in plain language and get working sync rules
- Groovy scripting for unlimited customization when needed
- Purpose-built for ITSM and DevOps platforms (Jira, ServiceNow, Freshservice, Freshdesk, Zendesk, Azure DevOps, Salesforce, Asana, GitHub, Ivanti)
- Custom connectors for specialized or proprietary systems
- Each party controls its own sync rules independently, which is critical for MSP relationships where you don’t want external parties modifying your logic
- Granular field mapping with conditional sync rules
- Enterprise security with ISO 27001:2022 certification
Exalate Cons
- Focused on work item synchronization; not a general data pipeline tool
- Requires installation on each connected platform
- Advanced customization benefits from Groovy knowledge (though Aida reduces this barrier)
- Pricing is based on connection complexity, which can add up for many MSP relationships
Best for: Organizations needing sophisticated, bidirectional ITSM synchronization with MSPs, partners, or customers. Particularly strong for scenarios where each party needs independent control over their sync rules, complex field transformations, or multi-platform integration networks.
Exalate maintains enterprise-grade security practices. Learn more at the Trust Center.

IBM App Connect
Organizations can use IBM App Connect to connect with MSPs. Since IBM provides managed services, you can integrate your system natively with this solution when IBM is part of your MSP ecosystem.
IBM App Connect Pros:
- Native integration with IBM services and platforms
- AI-powered connectors and templates
- Enterprise solution option for building custom integration tools
- Strong governance and audit capabilities
- Hybrid cloud support (on-premise and cloud)
IBM App Connect Cons:
- Strongest when IBM products are already in your stack
- Less intuitive than modern iPaaS alternatives
- Can require significant IBM ecosystem investment
- Implementation often requires IBM professional services
- Licensing complexity for mixed environments
Best for: Organizations already invested in IBM infrastructure or using IBM as an MSP who want native integration capabilities with greater control and autonomy.
Boomi
Boomi is an Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) solution that connects data with MSPs across multiple verticals. The platform emphasizes low-code development and has a strong presence in the mid-market.
Boomi Pros:
- User-friendly interface with drag-and-drop design
- Good balance of ease-of-use and customization
- Strong connector ecosystem for business applications
- Master data management capabilities
- API management features included
Boomi Cons:
- Bidirectional ITSM sync requires more configuration than specialized tools
- Can become complex for advanced cross-company scenarios
- Pricing tiers can be confusing
- Real-time sync capabilities vary by connector
- Better for internal integration than cross-company workflows
Best for: Mid-market organizations integrating with MSPs like SAP and Oracle NetSuite who want a balance between no-code simplicity and enterprise capability.
Oracle Data Integrator
This iPaaS solution handles high-volume batch integrations. Customers working with Oracle’s managed services can integrate their systems natively.
Oracle Data Integrator Pros:
- High-volume batch integration at enterprise scale
- Native Oracle ecosystem integration
- Git offline support for version control
- SAP delta extraction for incremental data loads
- Flow-based declarative user interface maps multiple targets in a single flow
Oracle Data Integrator Cons:
- Primarily batch-oriented; real-time sync is not the strength
- Best suited for Oracle-centric environments
- Steep learning curve for non-Oracle shops
- Less relevant for ITSM ticket synchronization
- Requires significant Oracle expertise
Best for: Enterprises with heavy Oracle investments needing high-volume batch data integration with MSPs in the Oracle ecosystem.
Choosing the Right Solution
The right MSP integration tool depends on your specific requirements:
| Requirement | Best Options |
| Simple app-to-app automation | Zapier |
| Large-scale data pipelines | SnapLogic, Talend, Informatica |
| Bidirectional ITSM/DevOps sync | Exalate |
| Oracle ecosystem integration | Oracle Data Integrator, Boomi |
| IBM ecosystem integration | IBM App Connect |
| Cross-company workflows with independent control | Exalate |
| Low-code mid-market integration | Boomi |
For MSP integration specifically, where you need real-time ticket synchronization, bidirectional data flow, and independent control for each party, purpose-built ITSM integration tools like Exalate typically outperform general-purpose iPaaS solutions.

Why is MSP Integration Important for Your Organization?
Organizations that rely on MSPs for critical business functions can expect these benefits:
A Unified Ecosystem
For companies using more than one MSP, integration gathers every key piece of data into a unified ecosystem. This keeps your internal teams and MSP representatives aligned on the same information.
Real-world application: A manufacturing company uses one MSP for ERP management and another for cybersecurity monitoring. Without integration, production delays caused by security incidents go unreported to the operations team. With integration, security alerts automatically create tickets in the ERP system, and the production team sees real-time status updates without switching between platforms.
Workflow Automation
Integrating data with an MSP enables workflow automation, which is essentially a different version of automated integration. Your team no longer needs to manually request reports and updates from the MSP. Data flows back and forth automatically with minimal human interference.
Real-world application: A healthcare provider integrates their patient management system with their IT support MSP. When critical system alerts trigger, tickets automatically escalate to the appropriate specialist team. Resolution updates sync back to internal dashboards, so staff always know the status without calling the help desk.
Better Flexibility and Scalability
A key consideration when integrating with a managed services provider is compatibility. Both parties must find ways to make their systems work together.
This compatibility work pays off. It makes collaboration more efficient and flexible. Your organization can scale up or downsize operations without having to decouple or restructure completely.
NVISO relies on Exalate to integrate deep tickets with customers. This automatically generates tickets and syncs comments, attachments, statuses, and other critical data.
Real-world application: A retail chain works with three MSPs: one for point-of-sale systems, one for inventory management, and one for customer analytics. During the peak holiday season, they need to scale support dramatically. Their integrated systems allow all three MSPs to see increased ticket volumes simultaneously and adjust staffing without manual coordination calls.
Higher Profits and Savings
MSP integration boosts ROI by improving the quality of services your MSPs provide.
For example, integrating data with a cybersecurity MSSP gives you up-to-date information about network outages, UI bugs, DDoS attacks, and other customer-facing issues. You can target spending to address these specific problems instead of using a shotgun approach.
Real-world application: A financial services firm integrates their trading platform with their infrastructure MSP. They track exactly which system components affect transaction processing speed. When latency issues cost them trades, they can immediately identify whether the problem is network, database, or application-related—and direct resources accordingly.
What Features Should You Look For in an MSP Integration Tool?
Not all integration tools suit every use case. Here’s what matters when evaluating options:
Bidirectional Synchronization
One-way data sync works for simple reporting scenarios, but real collaboration requires bidirectional flow. When your support team updates a ticket status, your MSP should see it immediately. When your MSP resolves an issue, your internal systems should reflect that change automatically.
Look for tools that handle true two-way sync without creating duplicate records or sync conflicts. The best solutions let you control sync direction on a field-by-field basis.
AI-Assisted Configuration
A traditional integration setup requires developers who understand both systems’ APIs. AI-assisted configuration changes this equation.
Tools like Exalate’s Aida let you describe your requirements in plain language: “sync all high-priority Zendesk tickets to Freshservice incidents.” The AI generates the configuration, which you can then refine through scripting for edge cases.
This approach cuts implementation time dramatically while still supporting enterprise-level customization.
Enterprise-Grade Security
Integration means data moving between systems—potentially across company boundaries. Security requirements include:
- Encryption in transit and at rest: TLS 1.2/1.3 minimum
- Role-based access controls: Limit who can modify sync rules
- Authentication standards: JWT tokens, multi-factor authentication support
- Compliance certifications: ISO 27001, GDPR compliance
- Data residency options: Control where sync processing occurs
Exalate maintains ISO 27001:2022 certification. For detailed security documentation, visit the Trust Center.
Scalability
Your integration needs will grow. A tool that handles 100 synced tickets per day might buckle under 10,000. Consider:
- How does pricing scale with volume?
- Can you add new MSP connections without architectural changes?
- Does performance degrade as sync volume increases?
- Can you handle burst scenarios (major incidents, seasonal peaks)?
Flexible Field Mapping
MSPs use different fields, statuses, and workflows than your internal systems. “Urgent” in one system might be “P1” in another. “Resolved” might map to “Closed” or “Completed.”
Look for tools that let you:
- Map fields with different names and data types
- Transform values during sync (status mapping, priority translation)
- Handle custom fields without code changes
- Filter which records sync based on conditions
Platform Coverage
Your MSP might use ServiceNow while you use Jira. Or Freshservice while your development team works in Azure DevOps. Check that your integration tool supports:
- Your current platforms
- Platforms your MSPs commonly use
- Platforms you might adopt as you grow
Exalate supports connections to Jira, ServiceNow, Salesforce, Azure DevOps (Cloud and Server), Freshdesk, Freshservice, Asana, GitHub, Zendesk, Ivanti, and custom connectors for specialized systems.

Calculate time and money savings from automated bidirectional sync.
MSP Integration Use Cases
Integration scenarios vary widely depending on your industry and MSP relationships. Here are patterns that work across different contexts.
Multi-Tier Support Escalation
Case: Your internal help desk handles L1 support, but complex issues escalate to an MSP for L2/L3 resolution.
Solution: Configure automatic escalation rules based on ticket attributes (priority, category, time in queue). Sync bidirectionally so your team sees progress without logging into the MSP’s system.
Application: A SaaS company routes infrastructure issues to their cloud MSP while keeping application bugs internal. Status updates flow back automatically, so customer-facing staff can provide accurate ETAs.
MSP Client Management
Case: You’re an MSP managing multiple clients who each use different ITSM tools.
Solution: Create integration connections for each client, routing tickets to appropriate queues based on client, priority, and issue type.
Application: An MSSP connects Jira Service Management to client Freshservice instances, ServiceNow deployments, and Zendesk accounts. Each client sees only their tickets, but the MSSP has unified visibility across all clients.
Development-Operations Coordination
Case: Customer-reported bugs need to reach developers, but support and development use different tools.
Solution: Sync customer tickets from your ITSM to your development platform. Map customer priority to development priority. Push the fix status back to support.
Application: Support uses Freshdesk, development uses Azure DevOps. When support identifies a software bug, a linked work item appears in Azure DevOps with customer context. When developers mark the item resolved, Freshdesk updates automatically.
Merger and Acquisition Integration
Case: After acquiring a company, you need to unify ticketing systems without forcing immediate platform migration.
Solution: Connect both platforms bidirectionally, allowing each team to continue using familiar tools while sharing ticket data.
Application: A technology company acquires a smaller firm. The parent uses ServiceNow; the acquisition uses Jira Service Management. Integration allows joint escalations while teams gradually align on processes.
What are the Challenges of Integrating With MSPs?
Plan for these hurdles before and during MSP integration:
Choosing the Right Integration Tool
Most systems don’t interoperate out of the box, so you can’t just pick any tool and expect it to work. Evaluate each product against your specific MSP platforms. Check connector availability, field mapping flexibility, and real-world performance at your expected volume.
Mitigation: Start with a proof-of-concept using your actual systems and data. Free trials help, but push them with realistic scenarios.
Managing Costs
While MSPs cut costs overall, wrong choices can lead to overspending. A subscription model might not suit you if a per-use model fits better. Integration tools add another layer of cost—some charge per sync, per connection, or per user.
Mitigation: Model your expected usage before committing. Include growth projections. Some vendors offer volume discounts that kick in as you scale.

Calculate time and money savings from automated bidirectional sync.
Communication and Process Alignment
If your organization lacks clear communication channels, integrating MSPs adds another layer of complexity. Teams need to agree on what data syncs, who owns which updates, and how conflicts get resolved.
Mitigation: Define data ownership and update responsibilities before technical implementation. Document which system is authoritative for each data type.
Preventing Security Risks
Every MSP integration introduces a potential point of failure. If the MSP experiences a security breach, your organization feels the consequences. More MSP connections means more potential attack surface.
Mitigation: Vet MSP security practices before integration. Implement least-privilege access. Monitor sync logs for anomalies. Ensure your integration tool supports encryption and authentication standards.
Avoiding Vendor Lock-in
Working closely with Fidelity Corp (from our earlier example) means aligning processes to create streamlined workflows. But this creates challenges when Soft Solutions decides to discontinue cooperation with Fidelity Corp and needs to decouple from their system.
Mitigation: Choose integration approaches that don’t hard-code MSP-specific logic into core systems. Keep data portable. Document integration dependencies.
Technical Complexity
Each platform has its own APIs, custom fields, and workflows. Integrating disparate ITSM platforms requires understanding nuances across multiple systems. For organizations with limited technical staff, keeping up with these differences can stretch capabilities thin.
Mitigation: Consider managed integration services (Integration-as-a-Service) where vendors handle setup and maintenance. This shifts complexity to specialists.
Best Practices For Integrating MSPs
To improve your chances of successful MSP integration:
- Use an effective model for integration and management: Find a service integration approach that independently handles and manages the integration of multiple MSPs. The SIAM approach to integrating MSPs increases accountability, optimizes costs, and improves service quality.
- Create detailed SLAs: As the bedrock of the agreement between your company and the MSP, ensure the SLA contains all deliverables, key metrics, and expected milestones. This helps prevent and resolve future conflicts. Review and update SLAs based on your company’s needs and market trends.
- Define roles and responsibilities: Ensure a clear understanding of who does what and the level of access they have. Create distinct definitions of roles and responsibilities for internal teams and the MSP’s representatives. This establishes a proper hierarchy for access and permissions, which supports security and transparency.
- Keep an internal governance structure: Even when an MSP handles your IT service, your internal team needs to monitor performance metrics and maintain control over your system. Ensure MSPs abide by privacy and compliance requirements.
- Start small and expand gradually: Begin with a limited scope—perhaps a single ticket type or one MSP connection. Validate that sync works correctly before scaling to more complex scenarios.
- Document everything: Integration logic, field mappings, escalation rules, and exception handling should all be documented. When team members change or issues arise, documentation prevents knowledge loss.

FAQs
What Are Managed Services Providers?
Managed services providers (MSPs) are companies that offer outsourcing services to other organizations. They handle various aspects of business operations, including IT, communication, marketing, HR, and cybersecurity.
Managed security services providers (MSSPs) are companies that outsource cybersecurity services to businesses, government agencies, public service companies, and others. Cisco is an example of an MSSP.
How Can I Integrate Managed Services Providers Using Exalate?
Exalate connects your internal ITSM or DevOps platform with your MSP’s system for automatic, bidirectional data synchronization. You install Exalate, create a connection between instances, and configure sync rules using Aida (AI-assisted configuration) or Groovy scripting. Once configured, tickets, status updates, comments, and attachments sync automatically based on your rules.
What Platforms Does Exalate Support for MSP Integration?
Exalate supports connections to Jira, ServiceNow, Salesforce, Azure DevOps (Cloud and Server), Freshdesk, Freshservice, Asana, GitHub, Zendesk, Ivanti, and more. You can also build custom connectors for proprietary or specialized systems using Exalate’s Script Engine, making it adaptable to virtually any MSP environment.
Can Exalate Integrate Multiple MSPs Simultaneously?
Yes. Exalate supports connecting multiple platforms at the same time. You can sync your internal systems with several MSPs, each using different ITSM tools, through separate connections from a single Exalate installation. Each connection has independent sync rules tailored to that specific MSP relationship.
How Does Exalate Handle Security for Cross-Company MSP Integrations?
Exalate maintains ISO 27001:2022 certification and implements enterprise security measures, including JWT access tokens, PATs, API keys, role-based access controls, HTTPS with TLS 1.2/1.3, and multi-factor authentication support. Each party controls its own sync rules independently, so your MSP cannot modify your configuration or access data beyond what you explicitly share. Learn more at the Trust Center.
Does Exalate Require Technical Expertise to Configure?
Exalate offers flexibility for different skill levels. Aida, the AI-assisted configuration tool, lets you describe sync requirements in plain language and generates working configurations. For advanced customization, Exalate uses Groovy scripting that gives you complete control over data transformation and sync logic. Most organizations start with Aida-generated configurations and refine with scripts as needed.
Recommended Reading:
- How to Get the Most out of Your Workflow Integration
- How Integration Service Providers Can Help Simplify Data Integration
- Exploring Ways To Implement Managed Services Integration
- Integration as a Service (IaaS): Everything Explained
- An Overview of Integrated Service Management (ISM)
- ITSM Integration: Simplify Your IT Services Like Never Before



