GitHub is popular amongst the software community for a good reason. It allows collaborating on software code with colleagues or even complete strangers. It comes loaded with project management and version control features as well.
GitHub Enterprise is GitHub packed, designed, and delivered for enterprise-level control over security, collaboration, and administration.
Jira, which comes with state-of-the-art project management features, is equally admired by the software community.
Note: Jira now refers to issues as “work items.” Throughout this article, we use “work items” and “work” instead of the older “issues” terminology.
So a GitHub Enterprise Jira integration can lead to snowballing team collaborations and engagements. It can help bridge the gap between the teams commonly using these platforms: the development team and the project management team.
Let’s look at why integrating GitHub Enterprise (Cloud) and Jira can be beneficial to these teams firsthand. Then we’ll cover the types of integration available, what to look for in a solution, and how to evaluate whether it fits your workflow.
Key Takeaways
- Integrating GitHub Enterprise and Jira gives both development and project management teams full visibility into each other’s progress without switching tools.
- Native integrations like GitHub for Jira handle basic linking and status updates, but fall short for advanced field mapping, conditional logic, or cross-company scenarios.
- The right integration tool should support bidirectional sync, granular field-level control, automated triggers, and error recovery to handle real enterprise workflows.
- Use cases span dev-to-QA handoffs, engineering-to-project management syncing, customer support escalation, multi-vendor coordination, and MSP service delivery.
- AI-assisted configuration tools have cut implementation time significantly, making complex integrations accessible without deep scripting knowledge.
- Evaluating total cost of ownership—not just licensing fees—helps determine whether an integration tool actually saves you money long-term.

Benefits of a GitHub Enterprise Jira Integration
Getting the best of both these tools can lead to better insights for smarter decision-making. Here’s why.
As mentioned, Jira has advanced features to manage work items through custom-made or predefined templates that are easy to follow and implement. It can also be used to implement tailor-made workflows suitable for any kind of team and has strong reporting capabilities, helping you set expectations beforehand.
GitHub Enterprise has a lot of features it already inherits from GitHub.com, like creating and managing unlimited repositories, project management capabilities, work tracking, version control, and more.
It can be deployed either on-premises or in the cloud. Both small and large organizations use it because, in essence, they all want smarter collaboration, elegant security features like the ability to control access at the organization-wide level, and multiple deployment options leading to simplified administration.
Why Integrate GitHub Enterprise and Jira?
If both these tools work hand-in-hand, it leads to full visibility of useful information and transparency in work that happens across teams and projects. The wealth of information lying in these individual tools, if acknowledged and integrated, can take your business profits forward and leave you with a richer customer experience.
But if you do it manually, it leads to costly, time-consuming errors that can surely be avoided if the right solution is in place.
A GitHub Enterprise Jira integration means automating the information exchange between these tools in real-time, bi-directionally, however, and whenever you want. It can also filter data shared between Jira and GitHub Enterprise, so it can be viewed in the most useful format.
You’ll also get the best of both tools, getting all the team members on the same page.
Before you jump to implementation, though, let’s look at use cases that clarify why integration is needed in the first place.
GitHub Enterprise Jira Integration Use Cases
Integration brings together diverse teams so they can access the same data in the tool of their choice and deal with it according to their specific needs.
Dev and Quality Assurance Teams
Case: GitHub Enterprise gives greater control at the organizational and user level, making it a preferred choice for managing source code. But that code needs to reach the QA team for testing, compliance checks, and bug detection, without manual handoffs slowing things down.
Solution: Integrate GitHub Enterprise and Jira so that commits, pull requests, and code changes flow automatically into Jira work items for QA review. Bugs raised in Jira get reflected in the GitHub environment for the dev team to act on. You define what triggers the sync—say, commits from certain managed users move work items to “Review” status in Jira for the QA team to pick up.
Dev and Project Management / Engineering Teams
Case: The dev team works best in GitHub Enterprise, but project management and engineering teams use Jira. Each has pre-decided workflows, and tracking progress would mean manually duplicating information about work or tasks back and forth.
Solution: With integration, information syncs automatically between GitHub and Jira. Status updates, assignments, and progress all stay current in both tools. You can maintain your existing workflows and still get correct status updates on both sides.
If you have developers belonging to different organizations in GitHub Enterprise, you can assign tasks based on role and expertise; they work within GitHub for commits and pull requests, and those changes are reflected in Jira for internal teams to prioritize the roadmap.
Dev and Customer Support
Case: Jira Service Management handles customer queries well, but the manual process of passing ticket information to the dev team is painful. Support agents end up writing long emails, hitting send, and then following up with more emails or phone calls.
Solution: Set up triggers so that when a ticket is assigned to a particular developer or has a certain label, a work item is created in GitHub automatically, with all the relevant context from the customer interaction. The dev team gets what they need without anyone copying and pasting anything.
Multi-Vendor Coordination
Case: Large enterprises often work with multiple external vendors, each using their own toolset. Coordinating development tasks across vendors who use GitHub Enterprise internally while your organization manages everything in Jira becomes a logistical challenge. Sharing too much data creates security risks; sharing too little creates blind spots.
Solution: Use an integration that gives each organization independent control over what data they send and receive. Your Jira instance sends only the relevant task details to the vendor’s GitHub environment, and vice versa. Each side controls its own sync configuration without needing access to the other’s system.
MSP Service Delivery
Case: Managed Service Providers (MSPs) juggle multiple client environments, each potentially running different tool combinations. An MSP that uses Jira for internal project management needs to sync with a client’s GitHub Enterprise instance without disrupting either side’s workflows or compromising data separation between clients.
Solution: Integration platforms that support multi-connection architectures let MSPs create separate, isolated connections for each client. Each connection has its own sync rules, triggers, and field mappings. One client’s data never touches another’s.
Real-world application: An MSP managing DevOps services for five clients creates dedicated integration connections between their Jira instance and each client’s GitHub Enterprise environment. Client A’s sprint tasks sync into a specific Jira project, completely separated from Client B’s data. The MSP tracks all client work in Jira with consistent workflows, while each client continues using GitHub without any changes to their process.
Types of GitHub Enterprise Jira Integration
Before choosing a tool, it helps to understand the types of integration available. Not all integrations work the same way, and the approach you choose depends on how deeply you need the two platforms to talk to each other.
Native Integration (GitHub for Jira)
GitHub offers a native app—GitHub for Jira—that links commits, branches, and pull requests to Jira work items. It works through reference keys: include a Jira work item key (like PROJ-123) in your commit message or branch name, and the link shows up in Jira’s development panel.
This is useful for basic traceability. Your project managers can see which commits relate to which work items without switching to GitHub. But it’s largely one-directional. It doesn’t create new work items in either tool, doesn’t sync custom fields, and doesn’t support conditional logic or triggers. For teams that need simple visibility into development activity from within Jira, it’s a decent starting point.
API-Based Custom Integration
If your organization has developer resources to spare, you can build a custom integration using the GitHub REST/GraphQL API and Jira’s REST API. This gives you complete control over what data flows between the two systems and how it’s transformed.
The trade-off is obvious: you’re building and maintaining an integration from scratch. That means handling authentication, error recovery, rate limiting, webhook management, and edge cases like field type mismatches. For a single, well-scoped integration that rarely changes, this can work. For anything that needs to evolve with your workflows—or scale across multiple projects—maintenance costs tend to spiral.
Third-Party Integration Platforms
Third-party platforms provide pre-built connectors for GitHub Enterprise and Jira, along with configuration interfaces that let you define sync rules without writing code from scratch. The better ones offer bidirectional sync, field-level mapping, automated triggers, error recovery, and support for multiple platforms beyond just GitHub and Jira.
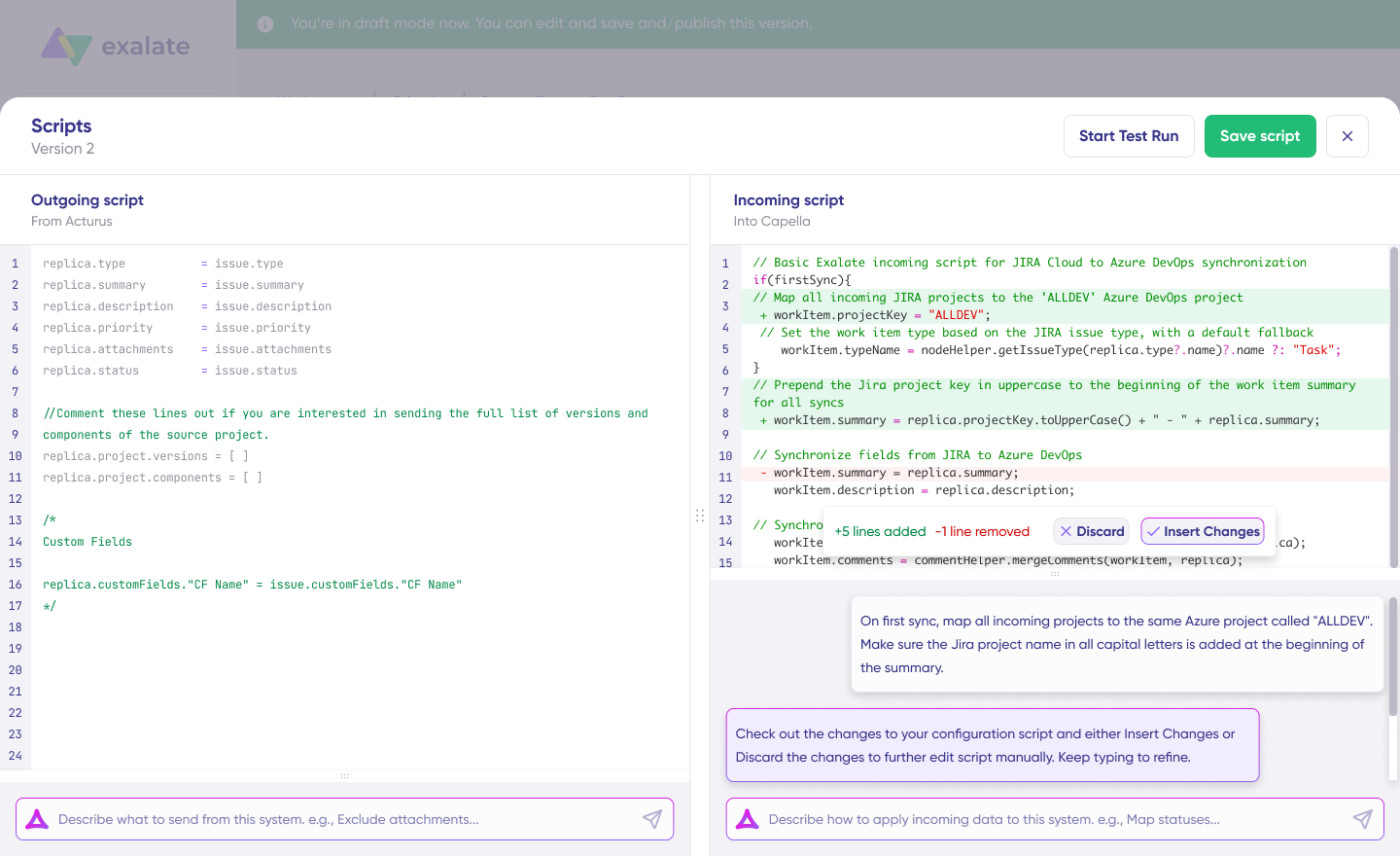
This is where tools like Exalate come in. They sit between your platforms and handle the complexity—data transformation, sync ordering, failure recovery—so your team focuses on defining what should sync and when, rather than building plumbing.

How to Choose the Right Integration Tool
When you have tools in place and various apps on their marketplaces, you most probably head there first. You might find it easiest to go with the native approach. But just because it’s available doesn’t mean it’s the right fit.
Here’s what to evaluate.
Does It Support Bidirectional, Real-Time Sync?
One-directional integrations (like native linking) solve visibility but not collaboration. If your QA team needs to push bug reports from Jira into GitHub, and your dev team needs to push status updates from GitHub back into Jira, you need bidirectional sync. And it should happen in real-time, not on a schedule that introduces delays and stale data.
Can I Control What Data Gets Shared, and How?
Not everyone on either side needs to see everything. The integration tool should let you define exactly which fields, statuses, and work item types are shared. You should be able to transform data as it moves between platforms: mapping GitHub labels to Jira priorities, for instance, or converting GitHub milestones to Jira fix versions. This kind of granular control also helps you protect sensitive information. Only the data you explicitly configure gets shared; everything else stays where it is.
Does It Handle Failures Gracefully?
Downtimes and failures are as much a fact as they are a pain. If an integration tool can’t recover from them cleanly, it’s not ready for enterprise use.
Look for a transactional sync engine that queues changes and applies them in the correct order after recovery. If your firewall goes down for maintenance or GitHub has an outage, the integration should pick up exactly where it left off, no duplicate data, no missed changes, no manual intervention.
Exalate, for instance, uses a transactional sync engine that breaks changes into atomic steps and includes an automatic retry mechanism to resume from the point of interruption.
How Secure Is the Data Exchange?
The information being shared must be secure. This isn’t optional for enterprise environments. Look for encrypted data transfer (HTTPS, TLS 1.2/1.3), token-based authentication (JWT), and role-based access controls. Just as important: check whether the vendor has independent security certifications. ISO 27001:2022 confirms that a systematic information security management system is in place. SOC 2 Type II validates that those controls actually work over time.
Exalate holds both certifications, and you can review its security posture in detail via the Trust Center.
Will It Scale Beyond GitHub and Jira?
Your integration needs today might be limited to GitHub Enterprise and Jira. But what about next quarter? If your support team uses Freshservice, your ops team runs on ServiceNow, and marketing is on Asana, you’ll want an integration tool that already supports those platforms instead of having to find and manage separate solutions for each.
Look for a tool that connects to a broad range of platforms—including Jira, GitHub, ServiceNow, Salesforce, Zendesk, Azure DevOps, Azure DevOps Server, Freshservice, Freshdesk, Asana, and more—so you can scale your integration network without starting over each time. Exalate supports all of these, plus custom connectors for proprietary systems with available REST APIs.
Does It Support AI-Assisted Configuration?
Modern integration platforms use AI to reduce the learning curve and speed up implementation. Instead of writing sync logic from scratch, you describe what you want in plain language and the AI generates the configuration for you.
Exalate’s Aida provides an AI-assisted configuration that generates sync rules from natural-language prompts. You describe your requirements—”sync task lists and assignees between Jira and GitHub”—and Aida produces the configuration, with suggested changes highlighted for your review.
You can accept, discard, or refine the output. This makes even complex integrations accessible without deep technical knowledge, though human review is always recommended before publishing changes.
How to Set up a GitHub Enterprise Jira Integration
If you’re on Exalate Classic, then you can import your existing nodes and connections using the “Import connection” feature.
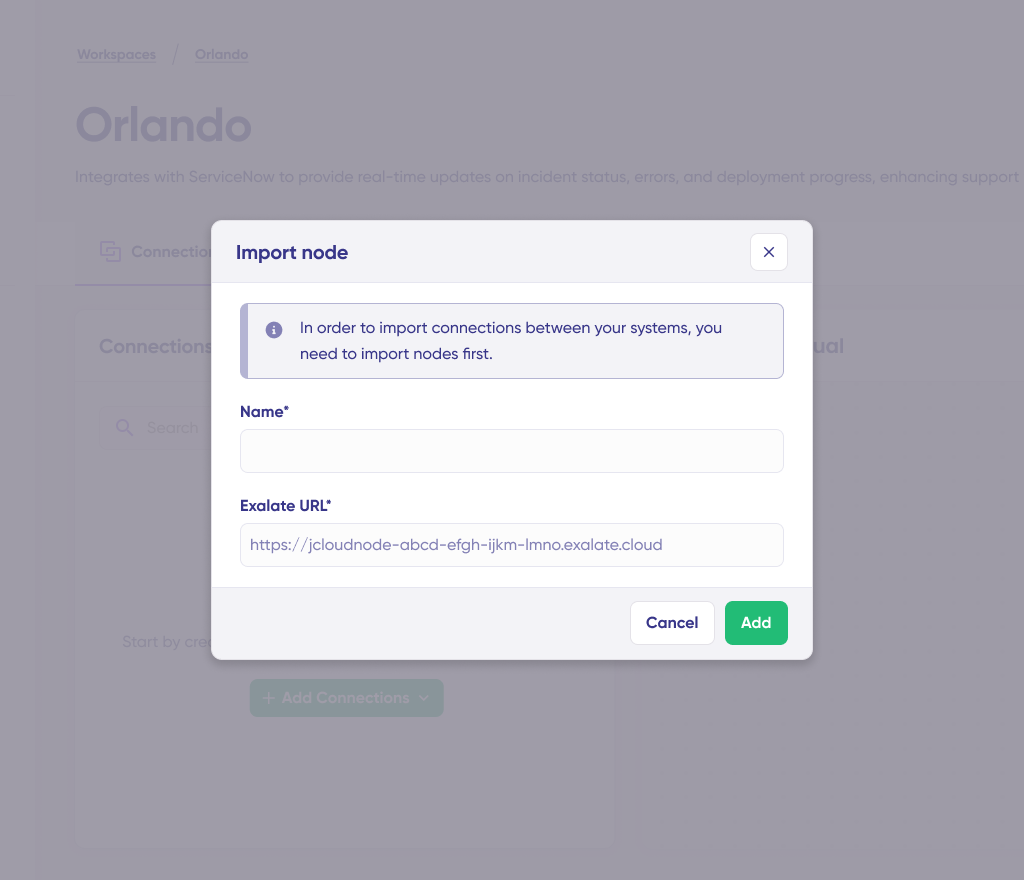
This will help you retain existing configurations and sync rules as you move to New Exalate.
To get started with Exalate for GitHub or discuss your use case and requirements, please contact sales.
GitHub Enterprise Jira Integration: What Can You Actually Sync?
One of the most common questions before starting an integration is: what data actually moves between the two platforms? The answer depends on your tool, but with a capable integration platform, you can sync:
- Work item data: Summaries, descriptions, statuses, priorities, labels, assignees, and custom fields. Changes in one tool update the corresponding work item in the other automatically.
- Comments and internal notes: Team discussions can flow between platforms, or you can choose to sync only external-facing comments while keeping internal notes private.
- Attachments: Files attached to work items in Jira can carry over to GitHub work items, and vice versa—useful when QA teams need screenshots or logs alongside bug reports.
- Pull request and commit references: Link pull requests and commits to Jira work items, so project managers see development activity without switching tools. Some integrations go further, syncing pull request statuses and review outcomes into Jira fields.
- Sprints and milestones: Map Jira sprints to GitHub milestones (or the other way around) to keep project timelines aligned across platforms.
- Custom fields and metadata: If your workflow relies on custom fields—cost centers, department tags, customer IDs—a flexible integration tool lets you map these fields between platforms, even when the field types don’t match exactly.
The key is that you control the mapping. You decide which fields sync, in which direction, and under what conditions. Nothing moves unless you’ve configured it to.
Why Exalate for GitHub Enterprise Jira Integration
We’ve touched on Exalate throughout this article, but here’s a consolidated look at why it fits this specific integration scenario.
Exalate is a bidirectional synchronization platform that connects GitHub Enterprise Cloud, Jira Cloud, and a wide range of other platforms, including ServiceNow, Salesforce, Zendesk, Azure DevOps, Azure DevOps Server, Freshservice, Freshdesk, Asana, and more, through its integrations ecosystem.
Independent sync control lets each side of the integration define what data they send and what they accept, without needing to coordinate changes with the other party. This is particularly valuable for cross-company integrations and MSP scenarios where each organization needs full control over its data exposure.
Aida (AI-assisted configuration) generates sync rules from natural-language prompts, making implementation faster and more accessible. Combined with a Groovy-based scripting engine for cases where you need maximum flexibility, it covers both simple and complex integration scenarios.
Transactional sync engine queues all changes, breaks them into atomic steps, and applies them in the correct order. If either system goes down, sync resumes from the exact point of interruption automatically. No data loss, no duplicates, no manual recovery.
Security is built in, not bolted on. Exalate is ISO 27001:2022 certified and SOC 2 Type II audited, uses TLS 1.2/1.3 encryption, JWT-based authentication, and role-based access controls. You can also review its security and architecture whitepaper for deeper technical details.
Multi-platform support means you start with GitHub Enterprise and Jira today and extend to Freshservice, ServiceNow, Asana, or Salesforce tomorrow—using the same platform, same configuration approach, and same security controls.
Conclusion
Both Jira and GitHub Enterprise are essential tools for code development and project collaboration. When integrated, they unlock useful business insights and let teams collaborate faster and more accurately.
But the integration tool you choose matters as much as the integration itself. It needs to be bidirectional, secure, flexible enough to handle your current and future requirements, and reliable enough to recover from failures without losing data.
Exalate covers all of that, plus the connector coverage to scale beyond GitHub and Jira as your integration network grows. If you want to estimate what integration could save your organization, try the pricing calculator to model the numbers for your specific scenario.

Frequently Asked Questions
How does Exalate connect Jira with GitHub Enterprise?
Exalate creates a bidirectional sync connection between your Jira Cloud instance and GitHub Enterprise Cloud. Once connected, you define what data flows between the two platforms: work items, statuses, comments, attachments, and custom fields using sync rules that you configure through Aida (AI-assisted configuration) or the Groovy scripting engine. Each side maintains independent control over what they send and receives.
Can I sync GitHub pull requests with Jira work items using Exalate?
Yes. Exalate can map pull request data, including status, reviewers, and branch information, to corresponding fields in Jira work items. This means project managers see development progress in Jira without switching to GitHub, and developers can track how their pull requests relate to project milestones without leaving their workflow.
What platforms does Exalate support besides GitHub and Jira?
Exalate connects Jira Cloud, GitHub Enterprise Cloud, ServiceNow, Salesforce, Zendesk, Azure DevOps, Azure DevOps Server, Freshservice, Freshdesk, Asana, and more. For proprietary or niche platforms, Exalate supports custom connectors for systems with available REST APIs. The full list is available on the integrations page.
What happens to my sync if GitHub or Jira goes down?
Exalate’s transactional sync engine queues all pending changes and tracks them in the order they occurred. When the affected system recovers, Exalate resumes synchronization from the exact point of interruption, applying changes in sequence. No data is lost, and no manual intervention is required.
Can different teams control their side of the integration independently?
Yes. Each side of an Exalate connection has its own sync rules defining what data to send and how to process incoming data. Yo ur Jira admin can change what fields they send to GitHub without needing to coordinate with the GitHub admin, and vice versa. This is especially useful in cross-company integrations where each organization needs autonomous control.
How long does it take to set up a GitHub Enterprise Jira integration with Exalate?
It depends on complexity. Simple integrations—syncing work items, statuses, and comments—can be operational within hours. More complex scenarios involving custom field mappings, conditional triggers, or multi-project configurations may take longer. Aida (AI-assisted configuration) significantly reduces implementation time by generating sync rules from plain-language descriptions of your requirements.
Can I use Exalate for cross-company integrations between separate organizations?
Yes. This is one of Exalate’s strongest use cases. Each organization installs Exalate on its own instance and creates a connection. Each side independently controls what data it shares and how it processes incoming data. The other party never gains access to your system; only the data you’ve explicitly configured to send moves across the connection.
Does Exalate support syncing custom fields between GitHub and Jira?
Yes. Exalate’s sync rules let you map any field available through the platform’s API. This includes standard fields like status and priority, as well as custom fields unique to your workflow: cost centers, department tags, environment details, or customer-facing labels. You can also transform data during sync, such as mapping GitHub labels to Jira custom field values.
How does Exalate pricing work for ServiceNow GitHub integration?
Exalate pricing is based on synchronized entities and connector usage rather than per-user licensing. Contact Exalate through the integrations page for specific pricing based on your ticket volume and integration requirements. Organizations can calculate potential ROI by quantifying time saved on manual updates, faster incident resolution, and improved cross-team collaboration before committing to implementation.
Recommended Reads:
- Jira Integrations: Integrate Jira and Other Systems Bidirectionally
- GitHub Salesforce Integration: How to Set up a Sync in 6 Steps
- How to set up a Jira Salesforce Integration
- How to Set up a ServiceNow GitHub Integration
- How to Set up a Jira GitHub Integration
- Jira ServiceNow Integration: How to Set up an Integration in 6 Steps
- Jira to Jira Integration: The Comprehensive Guide to Jira Sync



