With AI-powered integration tools cutting setup time, hybrid approaches combining commercial solutions with custom scripting, and the rise of citizen integrators, the traditional cost-benefit analysis for integration no longer applies.
This guide provides a data-driven framework to help you make the right choice for your organization. Whether you’re an MSP managing dozens of client integrations, an enterprise IT team scaling connections across departments, or a growing SaaS company expanding its tech stack, you’ll find practical guidance here.
We’ll break down whether it makes sense to build a custom integration using your own resources or buy a commercially available solution. We’ll also look at how the build vs. buy debate plays out in cross-company integrations, where the stakes (and complexity) are significantly higher.
Note: Jira now refers to “issues” as “work items.” Throughout this guide, we use the updated terminology—”work items,” “work item types,” and “work”—to reflect this change.
What you’ll learn:
- A scored decision framework to objectively evaluate build vs. buy for your specific use case
- Hidden costs that most organizations miss in their initial analysis
- How AI-powered integration reduces both build and buy timelines
- Real ROI calculations showing when each approach makes financial sense
- Hybrid integration strategies that combine the best of both worlds
Key Takeaways
- Integration projects involve seven distinct phases, from requirements gathering to ongoing customization, each one adding cost and complexity that most teams underestimate upfront.
- Building custom integrations gives you full control, but scaling across multiple partners, applications, or departments creates exponential maintenance overhead.
- Buying a commercial integration solution accelerates deployment, reduces long-term costs, and frees your dev team to focus on core product work.
- The hidden cost trap is real: initial development typically accounts for only 30–40% of the total cost of ownership for custom integrations, with maintenance eating the rest.
- A hybrid approach, using a commercial platform with deep scripting capabilities like Exalate, bridges the gap between out-of-the-box speed and custom-built flexibility.
- AI-assisted configuration tools like Aida cut integration setup time significantly, making even complex cross-company scenarios accessible without deep scripting knowledge.

Quick Decision Guide
Choose to BUILD the integration yourself if:
- No commercial solution exists for your specific use case ✓
- You have a dedicated dev team available and ready to prioritize this long-term ✓
- It’s a simple, one-time connection between two internal systems ✓
Choose to BUY from an integration vendor if:
- You need fast deployment without a steep learning curve ✓
- Your dev resources are limited or better spent on core product work ✓
- Multiple systems need to be connected (Jira, ServiceNow, Salesforce, Azure DevOps, Zendesk, Freshservice, GitHub, and more) ✓
- Cross-company integration is required ✓
- Your requirements evolve frequently and need to keep up with changing workflows ✓
- You need both speed AND customization, a platform with deep scripting capabilities ✓
Integrations are complex. Technical challenges, diverse organizational structures, people with varying skill sets and agendas, distinct processes, and separate applications all add to this complexity.
Before we dig into the build vs. buy decision, let’s walk through the actual phases of an integration project because understanding the full scope is what separates a good decision from a costly one.

Calculate time and money savings from automated bidirectional sync.
Phases of the Integration Project
Gather Requirements and Plan
- Start by identifying the pain points. What’s the most difficult part of your integration? Is it assigning new users to platforms? Copying data between applications? Sharing information via email and chat just to keep track of statuses? Or going back and forth between different workflows until it becomes confusing for everyone?
- Then look at the communication path. What deployment models do you and the other environments you’re integrating with use? What security, authorization, and authentication challenges are likely to come up? For cross-company scenarios, you’ll need to think about how data governance policies differ between organizations and whether the integration platform supports end-to-end encryption and role-based access controls.
- Plan both internal and external resources. Work out not just the budget, but the amount of work and effort required. Make sure the right people are involved from the start—including stakeholders from both sides if it’s a cross-company integration.
Design the Integration
- Work out your common data model. Carefully map data exchanges and transformations between systems. A three-space text field won’t map to a two-digit text field, and no amount of wishing will make it so. If you’re connecting Jira to ServiceNow, for example, mapping work item types to incident categories requires careful planning, especially when each side has different custom field structures.
- Figure out redundancies and failure handling. Identify potential failure paths and proper notification protocols. You need a formal rollback system in place because no system is perfect. Platforms with built-in transactional sync queues where changes are tracked in order and automatically retried after downtime. If you’re building custom, you need to engineer all of this from scratch.
- Design the integration scope. Look at all the data you’ve gathered and determine your unique information flow requirements. Do you want one-way or bidirectional synchronization? Which fields do you want to sync and which should be excluded?
These are critical questions to answer before you begin, especially for compliance-sensitive environments where you need granular control over what crosses organizational boundaries.
Implement the Integration
Your developers can now start coding the integration or configure a commercial solution with the required functionality. This might seem straightforward, but the hard part is figuring out how to handle errors and exceptions without causing the applications to terminate.
With a commercial platform like Exalate, AI-assisted configuration through Aida can generate working sync scripts from natural language prompts—reducing this phase from weeks to hours for many scenarios.
Validate Your Integration Solution
Testing is where many integration projects hit unexpected snags. You need to subject the process to testing for performance, functionality, and future pain points. Testing to ensure there are no unexpected errors is critical. A system crash during a cross-company sync can lead to data inconsistencies that are extremely difficult to untangle after the fact.
If you’re building custom, you’re responsible for designing the entire test framework. Commercial solutions typically come with built-in validation tools and error reporting.
Manage Your Production Release
Your integration solution is validated and ready for production. Sometimes, the release also involves deployments across company borders (cross-company integrations).
It needs to be delivered to your end users in a way that’s transparent and easy to understand for everyone. Disruptions cost, and you need to account for that, not just for your business, but for any businesses you’re integrating with. Rollback plans are essential. If unforeseen failures or consequences occur, you need to be covered.
Maintain the Integration
Ask anyone in software and engineering circles, and you’ll hear the same thing: maintenance is where the real cost lives. According to Forrester’s Total Economic Impact model (2024), roughly 78% of lifetime software TCO accumulates after launch, not during initial development.
For custom integrations, maintenance includes handling API changes from connected platforms, security patches, feature requests as workflows evolve, and documentation updates when team members change. Make sure you have a maintenance plan in place from day one.
Customize the Integration
Here’s the thing about integration: once you’ve started, that’s not the end. You’re going to start getting requests to make it better—new workflows, permissions, data fields, and different insights into existing workflows. Take these inevitable customization requests into account when you’re making the build vs. buy decision, because they’ll keep coming.
How Do Companies Approach an Integration Project?
Companies integrate their daily applications to overcome specific pain points. When teams exchange data manually across platforms like Jira, ServiceNow, Salesforce, Zendesk, or Azure DevOps, it leads to inaccuracies, delays, missed deadlines, and poor business outcomes.
For smoother collaboration with other companies using different applications entirely, the need for integration becomes even more urgent. The expectation: automatic, real-time data exchange based on defined requirements.
Integration requirements vary in complexity and are volatile. They can range from simple data mapping between entities to creating complex multi-level dependencies between the same entities.
A Jira-to-ServiceNow sync might start with basic work item-to-incident mapping, then grow to include bidirectional status updates, comment syncing, custom field transformations, and conditional routing based on project or priority.
Companies usually start looking for automation solutions. This approach works for basic one-directional mappings, but often hits a wall for complex, evolving requirements.
They might hit the limit of what simple automation tools can do, lose hope of finding a solution that handles advanced use cases, and conclude that building in-house is the only option.
But that conclusion often skips a critical step: evaluating commercial platforms that offer deep customization, not just templates. This blog is for companies in exactly that situation, weighing:
- Building the integration in-house: Creating a custom integration application using your own developers. This typically involves accessing applications’ open APIs and writing code to enable automatic information sharing between them.
- Buying a COTS (Commercial Off-the-Shelf) integration solution: Purchasing a commercially available solution that provides integration-as-a-service. Specifically, a solution that offers the automation and customization depth you actually need, not just drag-and-drop templates that break when requirements get complex.
Weigh the Options: Building Vs. Buying an Integration Solution
To make a sound build vs. buy decision, you need to evaluate a range of factors—not just the sticker price. Let’s deconstruct both approaches.
Why Do Companies Choose to Build a Custom Integration Solution?
Usually, MSPs (Managed Service Providers) or MSSPs (Managed Security Service Providers) opt for building in-house. They do so for various reasons: availability of resources, security considerations, or the belief that their use case is too unique for commercial tools.
Building your own integration can make sense when:
- You need a genuinely bespoke integration that no commercial solution can handle. This is rarer than most teams assume, but it does happen, especially for proprietary legacy systems with non-standard APIs.
- You have a dedicated team of engineers, developers, system architects, and product managers ready to develop and maintain the integration. This team needs to be committed long-term, not borrowed from other projects, because integration maintenance is demanding and ongoing.
- The integration is basic and connects to a single application. If you’re building a one-off connector between two internal tools with simple data mapping, the code complexity stays manageable at first.
- You have strict security or compliance requirements that require full control over data handling, encryption, and access policies. That said, commercial solutions with ISO 27001:2022 certification and on-premise deployment options can often meet these requirements without building from scratch. It’s worth verifying before committing dev resources.
- You want complete ownership of the code, support, maintenance, and roadmap.
Drawbacks of Building a Custom Integration Solution
Here’s where the build approach typically runs into trouble:
- Scaling is hard. Whether you’re adding a new application to your stack (say, Freshservice or Asana alongside your existing Jira and ServiceNow setup) or connecting with a new customer, you may end up rebuilding similar solutions over and over. Each new connection is essentially a new project, and the complexity compounds exponentially. What worked for 2 systems falls apart at 5, 10, or 50.
- Business environments are dynamic. Workflows change, priorities shift, and your integration needs to change with them. Your dev team has to absorb every change request on top of their other responsibilities. This takes time and creates bottlenecks.
- Resource competition and knowledge drain. Your developers have other work to do. Integration maintenance competes with core product development, and in a fast-paced environment, integration tickets often lose out. Worse, when the original developer leaves, they take critical system knowledge with them. Custom integrations become black boxes that nobody wants to touch.
- Maintenance costs are high. When you need upgrades (and you will—for security, performance, or compatibility reasons), you have to modify existing code that was built for the original system. Sometimes you’re replacing components entirely. This means retesting, revalidating, and updating documentation, all of which need to be factored into the total cost of ownership.
- Documentation falls behind. This isn’t just about the code. When your original dev team changes, the incoming team inherits a system they didn’t design. Without excellent documentation (which rarely stays current for custom projects), they’re reluctant to modify anything—creating technical debt that compounds over time.
- When integration, especially across company borders, becomes essential to your workflows, you face a real decision. Building might seem cheaper initially, but as we’ve seen, maintenance is what eats your budget long-term. A successful business is a marathon, not a sprint.
A lot of these difficulties can be avoided by using the right commercial integration platform. While acquisition costs are higher upfront, they start to even out when you factor in customization, maintenance, API change handling, and the opportunity cost of your dev team’s time.
Benefits of Buying a Third-Party Integration Solution
Here’s what a commercial integration platform brings to the table:
- Agility and scalability. Adding another application or partner to your integration is straightforward, whether it’s connecting Jira to Salesforce today and Azure DevOps to Freshdesk tomorrow. You’re not rebuilding from scratch each time.
- Developer time goes to core work. Your engineering team focuses on product development instead of integration, plumbing, and maintenance overhead. This directly impacts your product roadmap velocity and your ability to ship what customers actually pay for.
- Faster deployment. Commercial platforms already have the connectors, error handling, and sync infrastructure built. What might take your team months to build from scratch can be configured in days or even hours, especially with AI-assisted configuration tools.
- Resilience to system changes. When Jira releases a new API version or ServiceNow updates its data model, the platform vendor handles the compatibility work. You don’t have to scramble to patch custom code every time a connected application pushes an update.
- Independent control over your data. With the right platform, each side of a cross-company integration defines what data they send and receive. Changes in your internal processes don’t break the integration for your partner, and vice versa. This is critical for MSP-to-client connections and partner ecosystems where each organization needs to maintain autonomy.
- Predictable cost structure. Commercial solutions offer defined pricing plans with support included. You know what you’re paying annually, and you can plan for it, unlike custom builds, where a single unexpected API change can trigger a multi-week development sprint.
- Vendor-maintained documentation and support. The platform vendor keeps documentation current, provides training resources, and offers support teams for troubleshooting. When your team member who managed the integration leaves, the platform documentation and vendor support create continuity that custom builds simply can’t match.
- Built for change. Good commercial platforms are designed with underlying system changes in mind. They operate independently of changes to the connected applications, so your integration stays functional even when the systems it connects are evolving.
Challenges of Buying a Third-Party Integration Solution
Buying software is essential for modern integration requirements, but there are real challenges to address:
- Template limitations. Many commercial tools rely on pre-built templates. If you have an advanced use case with detailed data mappings and dependencies, template-based solutions can’t handle it. You’re constrained by the UI and the vendor’s assumptions about what you need. The key differentiator here is whether the platform offers deep scripting capabilities alongside its templates, or whether templates are all you get.
- Market noise. With dozens of integration platforms available—iPaaS solutions, unified APIs, embedded integration platforms, and cross-company sync tools—choosing the right one is difficult. You need to evaluate not just features, but whether the platform can handle your specific complexity level, supports the applications you use (Jira, ServiceNow, Salesforce, Azure DevOps, Zendesk, Freshservice, Freshdesk, GitHub, Asana, and others), and grows with your requirements.
| One of our customers asked: “But can’t we build our integration ourselves?” And we replied: “Yeah, you can do everything via the REST API. That’s fine. But then you also need to think about bidirectional information exchange. With the REST API, you can push and get stuff. But you need to develop all of this yourself. So you’re basically rebuilding Exalate.” |
The Hybrid Approach: Why It’s No Longer Build OR Buy
One of the biggest shifts in the integration landscape is the rise of hybrid strategies. According to a Neontri analysis of enterprise software decisions, most organizations land in the “hybrid zone” where they need both speed and customization, and pure build or pure buy doesn’t fully serve them.
The hybrid approach works like this: you buy a commercial integration platform for the heavy lifting—connectors, error handling, sync infrastructure, security, and maintenance—then use the platform’s scripting capabilities to build custom logic for your unique requirements.
This is where Exalate’s model stands out. Instead of choosing between rigid templates (pure buy) or coding everything from scratch (pure build), you get a commercial platform with a Groovy-based scripting engine that lets you customize sync rules at any level of complexity.
Need conditional field mappings based on business logic? Dynamic project routing? Custom data transformations that match your internal taxonomy? You script it within the platform, and Exalate handles the connectivity, error handling, and system change resilience underneath.
When hybrid makes sense:
- You have advanced use cases that templates can’t handle, but you don’t want to build an entire integration stack from scratch
- Your integration needs evolve frequently, and you need a platform that grows with you without requiring architectural redesigns
- You’re integrating across company borders, where each side needs independent control, but the core sync mechanism needs to be reliable and maintained by someone else
- You want your team to focus scripting effort on business logic, not on building and maintaining plumbing
The hybrid model effectively eliminates the biggest drawbacks of both approaches: the maintenance burden of custom builds and the inflexibility of template-only tools.
Total Cost of Ownership: The Real Build Vs. Buy Math
The most common mistake in build vs. buy decisions is comparing initial costs. According to Forrester’s Software Development Trends Report (2024), 67% of failed software implementations stem from incorrect build vs. buy decisions, largely because teams underestimate the total cost of ownership (TCO).
What TCO Actually Includes
For building custom:
- Initial development (developer salaries, infrastructure setup, testing)
- Ongoing maintenance (15–20% of initial build cost annually, per Forrester estimates)
- API change management (every connected platform will update its APIs; you absorb the cost)
- Security patching and vulnerability management
- Documentation creation and ongoing updates
- Knowledge transfer when team members leave (tech industry turnover is ~36% annually)
- Opportunity cost (what your developers aren’t building while they maintain integrations)
- Scaling costs (each new integration partner or application is essentially a new project)
For buying commercial:
- License or subscription fees
- Initial configuration and customization
- Training for your team
- Potential customization beyond standard features (scripting, API work)
- Vendor management overhead
The Numbers in Context
Research consistently shows that initial development represents only 30–40% of the total cost of ownership for custom integrations. Maintenance, updates, and adaptations account for the remaining 60–70%. McKinsey (2024) notes that large IT projects run approximately 45% over budget and 7% over schedule, while delivering 56% less value than originally predicted.
For a cross-company integration connecting Jira, ServiceNow, and Salesforce—a common enterprise scenario—building custom typically involves:
- 3–6 months of initial development
- 1–2 dedicated developers for ongoing maintenance
- Full rebuilds when any connected platform makes breaking API changes
- No support beyond what your team provides
The same integration using Exalate involves:
- Days to weeks for configuration (less with Aida’s AI-assisted setup)
- Vendor-maintained connectors that absorb API changes automatically
- Built-in error handling and retry logic
- Support and documentation from the vendor

Calculate time and money savings from automated bidirectional sync.
Practical Use Cases: Build Vs. Buy in Action
Use Case 1: MSP Connecting Multiple Clients Across Different Platforms
Case: An MSP manages IT services for 15 clients. Clients use a mix of Jira, ServiceNow, Freshservice, Zendesk, and Azure DevOps. The MSP needs bidirectional work item syncing with each client, independent of their platform choice.
Solution: Building custom integrations for 15 different client environments across 5+ platforms is a scaling nightmare. Each client connection is a separate development project. Using Exalate, the MSP configures each client connection independently. Aida generates sync scripts based on natural language descriptions of each client’s requirements. Each client controls their side of the integration without affecting others.
Use Case 2: Enterprise IT Connecting Development and Service Management
Case: A financial services company runs engineering on Jira Cloud, IT service management on ServiceNow, and customer support on Zendesk. They need work items from Jira to automatically create incidents in ServiceNow when they impact production, and customer-reported issues in Zendesk to generate Jira work items for the engineering team.
Solution: This three-way sync involves conditional routing (not all Jira work items should create ServiceNow incidents), bidirectional status updates, and different data models across platforms. Building this custom requires deep knowledge of three different APIs and constant maintenance as each platform evolves.
Exalate handles the connectivity and error handling natively, while the scripting engine accommodates the conditional logic and field transformations specific to this workflow. Data stays encrypted end-to-end, and each team maintains control over their own sync rules, critical for a financial services environment where regulatory compliance matters.
Use Case 3: Cross-Company Integration for a Vendor Relationship
Case: A software company partners with an outsourced QA vendor. The software company uses GitHub for code and Jira for project management. The QA vendor uses Azure DevOps. Bug reports need to flow from Azure DevOps into Jira as work items, with status updates syncing bidirectionally.
Solution: Cross-company integration adds a layer of complexity that most custom builds aren’t designed for. Both organizations need to maintain independent control over their data—the QA vendor shouldn’t have access to the software company’s internal Jira environment, and vice versa.
Exalate gives each side independent sync rules. The software company defines what they receive and how it maps to their Jira work items. The QA vendor controls what they send from Azure DevOps. Neither side can see nor modify the other’s configuration.
How AI Is Changing the Build Vs. Buy Equation
The integration landscape has fundamentally shifted with AI-powered tools. What once took weeks of manual scripting can now be accomplished in hours, and this dramatically impacts the build vs. buy calculation on both sides.
The Before and After
Traditional script-based integration (pre-AI): Average setup for complex integrations ran around 20 hours. It required advanced scripting knowledge, had a high barrier to entry for non-technical users, and involved extensive documentation research.
AI-powered integration (current): The same integration can be configured in 5–10 hours. Natural language prompts generate working sync scripts. It’s accessible to integration users without deep scripting experience. And context-aware recommendations based on your existing configuration reduce trial and error significantly.
How Exalate’s Aida Works
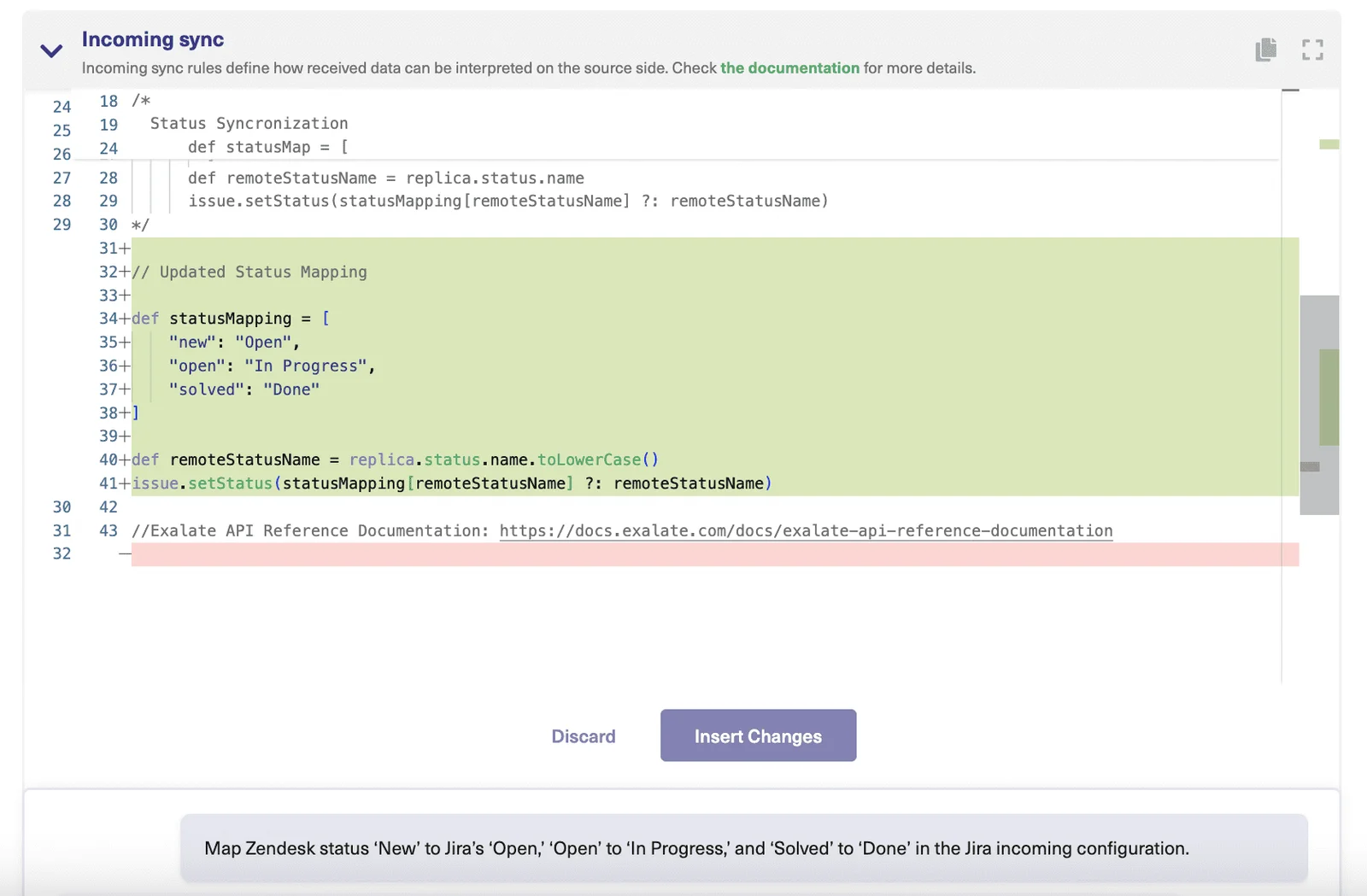
Aida is Exalate’s AI-powered configuration assistant. It generates sync scripts based on natural language prompts, analyzes your existing configurations, and suggests optimized scripts with color-coded change tracking for easy review.
Example prompt to Aida: “Sync high-priority incidents from ServiceNow to Jira as bug work items. Map ServiceNow ‘Short Description’ to Jira ‘Summary’, sync all internal comments, and update the status bidirectionally. Only sync incidents assigned to the IT Operations team.”
Aida generates the working script. You review it, test it, and deploy. No deep Groovy knowledge required, though the scripting engine is fully available for teams that want to fine-tune beyond what Aida generates.
AI Capabilities That Bridge Build Vs. Buy
What makes AI-assisted integration particularly powerful is how it handles scenarios that traditionally pushed teams toward building custom:
- Multi-level data transformations — mapping complex data structures between systems with different schemas
- Conditional field mappings — applying different sync rules based on business logic (priority levels, project categories, team assignments)
- Dynamic project routing — automatically dispatching synced items to the correct project or queue based on configurable criteria
- Custom workflow synchronization — matching different status workflows across platforms that don’t share the same terminology
- Cross-company integration rules — defining what each side sends and receives, independently
- Data format conversions — handling differences in date formats, field lengths, and data types between connected systems
The practical impact: setup time drops by 50% or more, the AI follows scripting best practices (reducing bugs), non-technical users can create sophisticated integrations, and patterns can be quickly replicated for new connections. The learning curve for new team members flattens dramatically compared to learning scripting from scratch.
Important: Always review and test generated scripts before deploying to production. Testing in a staging environment first is a best practice for any integration, whether built or bought.
Common Build Vs. Buy Integration Mistakes to Avoid
Mistake #1: Underestimating Maintenance Costs
The reality: Initial development typically represents only 30–40% of the total cost of ownership for custom integrations. Maintenance, updates, and adaptations account for the remaining 60–70%.
What gets missed: API changes from connected applications that require code updates. Security patches and vulnerability management. Feature requests from stakeholders as workflows evolve. Documentation updates when team members change. Regression testing after any system update on either side of the integration.
Mistake #2: Choosing Based on Initial Costs Alone
The reality: Solutions with the lowest sticker price often hit limitations when your integration use case gets complex.
Common scenario: You start with a free or cheap automation tool ($0–$500/year). It works for basic syncing. As requirements grow, you need conditional logic, bidirectional status mapping, and cross-company data controls. The tool can’t handle it. You rebuild with a more capable platform or custom code. The total cost: original tool + rebuild time + vendor switching costs + opportunity cost of delays.
The fix: Evaluate TCO over 3–5 years, not initial price. Include migration costs if you’re likely to outgrow the solution.
Mistake #3: Underestimating Complexity
The reality: Most custom integration projects take longer than initially estimated. McKinsey (2024) data shows that large IT projects run roughly 45% over budget.
Where complexity hides: Edge cases discovered during development. Different data models between systems require transformation. Authentication and security requirements, especially for cross-company scenarios. Error handling and retry logic that prevents data loss. Performance optimization for high data volumes. And the biggest one: cross-company synchronization, where you’re dealing with two different organizational processes, security policies, and change management cycles simultaneously.
The fix: If your integration is complex, evaluate commercial solutions with deep customization capabilities, not just template-based tools.
Mistake #4: Not Planning for Scale
The reality: What works for connecting 2 systems breaks down at 5, 10, or 50.
Scaling traps: Each custom integration you build adds exponential complexity. There are no reusable patterns or architecture; every connection is a one-off project. Knowledge gets siloed with individual developers. Maintenance becomes unsustainable as the portfolio grows.
The fix: If you need to integrate more than 3–4 systems, or plan to add integrations over time, choose a platform approach that scales architecturally, where adding a new connection doesn’t require rethinking your entire setup.
Mistake #5: Forgetting About Knowledge Transfer
The reality: Custom integrations without excellent documentation become “black boxes” that no one wants to touch when the original developers leave.
What happens: New developers are reluctant to modify code they didn’t write and don’t understand. Business-critical integrations become fragile. There’s a high risk of breaking production systems during updates. In the worst case, you’re looking at a complete rebuild.
The fix: If building custom, allocate 15–20% of development time to documentation. Or choose a commercial solution where the vendor maintains documentation, provides a support community, and offers training, creating continuity that doesn’t depend on any single person on your team.
Mistake #6: Ignoring Vendor Lock-In Risks
The reality: Not all commercial platforms are equal when it comes to flexibility. Some lock you into their ecosystem with proprietary data formats, limited export options, or pricing models that penalize you for growing.
What to evaluate: Can you export your integration configurations? Does the platform use open standards? What happens to your data and sync history if you switch vendors? Are pricing tiers transparent, or do costs spike unpredictably as you scale?
The fix: Choose platforms that offer transparent pricing, open APIs, and configuration portability. Evaluate exit costs as part of your TCO analysis.

How Exalate Solves the Build Vs. Buy Dilemma
Exalate bridges the gap between rigid templates and full custom builds. It handles the most complex cross-company integration use cases flexibly and adaptively, making it the go-to platform for MSPs connecting with customers, enterprise IT teams bridging departmental tools, and organizations that need deep customization without the overhead of building from scratch.
Exalate supports integrations between Jira Cloud, Salesforce, ServiceNow, Zendesk, GitHub, Azure DevOps (Cloud and Server), Freshservice, Freshdesk, Asana, and other platforms through custom REST API connectors. If a system has an API, Exalate can connect to it.
With Aida, Exalate’s AI-assisted configuration tool, you can set up advanced integrations using natural language prompts. Aida generates scripts based on your input, existing configurations, and Exalate’s scripting API, so you don’t need to be a scripting expert to build sophisticated sync rules.
Each organization in a cross-company integration maintains independent control over its side. You define what data you send and receive through your own sync rules and field mappings. The other party can’t override or access your settings.
This makes Exalate particularly well-suited for MSP-to-client connections, partner ecosystems, and M&A scenarios where systems need to connect before full organizational alignment.
All data moves over TLS 1.2/1.3 encryption, authentication uses JWT tokens with automatic rotation, and Exalate holds ISO 27001:2022 certification. For organizations that need maximum data control, on-premise and Docker deployment options are available. Full security details are available in the Exalate Trust Center.
A Time and Cost-Saving Analysis
Assuming a conservative estimate of 10% time savings for each employee working with integrated systems, and an average salary of $60,000 per employee, the potential cost savings for a team of 20 people:
Time savings per employee per year: 10% x 2,080 hours = 208 hours. Total time savings for the team: 208 hours x 20 employees = 4,160 hours. Cost savings from reduced labor hours: 4,160 hours x $30 per hour (fully loaded cost of labor) = $124,800 per year. |
Exalate can also help reduce licensing fees for tools that are no longer needed due to integration. Assuming an average licensing fee of $50 per month per user, and a reduction of 10 licenses across different tools:
Licensing fees saved per year: 10 licenses x $50/month x 12 months = $6,000 per year. Combined potential cost savings: $130,800 per year. |
If the cost of purchasing an Exalate license is $3,100 per year:
ROI = (Total Cost Savings – Cost of Exalate) / Cost of Exalate x 100% = ($130,800 – $3,100) / $3,100 x 100% = 4,118% |
For every $1 spent on Exalate, your company could potentially receive a return of $41.18 in cost savings and increased efficiency.

Calculate time and money savings from automated bidirectional sync.
Exalate for Different Organization Types
For MSPs and MSSPs
Connect with multiple clients using different applications: Jira, ServiceNow, Freshservice, Freshdesk, Zendesk, Azure DevOps, and more. Each client connection is independently configured. Scale easily as you add new clients with no architectural limits. Aida helps quickly set up similar integrations across different client environments.
For Enterprise IT Teams
Integrate departments using different tools (ServiceNow for ITSM, Jira for development, Zendesk for support, Salesforce for CRM). Maintain departmental autonomy while enabling collaboration across teams. Handle complex approval workflows or change management handoffs across systems. Support M&A scenarios where different system landscapes need to connect before organizational alignment is complete. Embed Exalate as a white-label integration capability.
For Financial Services & Banking
Meet stringent regulatory compliance requirements with ISO 27001:2022 certification. Deploy on-premise for maximum data control. Connect ServiceNow (IT service management) with Azure DevOps (application development) for secure financial software delivery. All data encrypted with TLS 1.2/1.3; JWT tokens with automatic rotation for authentication.
For Government & Public Sector
Deploy on-premise for maximum data sovereignty. Integrate legacy government systems with modern cloud platforms. Enable secure inter-agency collaboration and data sharing. Support both classified and unclassified network requirements with flexible deployment options.
For Manufacturing & Supply Chain
Connect ERP systems with project management and quality assurance tools. Integrate production planning with supplier and vendor systems. Enable real-time visibility across global supply chain operations. Synchronize quality work items, production incidents, and corrective actions. Link Jira (quality management) with ServiceNow (asset and maintenance management) for real-time production visibility.
The Final Verdict: Build or Buy an Integration Solution
We’re almost at the end of our dilemma. I hope this blog has steered you in the right direction. If not, read on.
Modern integration requirements are evolving and demanding. So we ask a few questions and choose the correct answer: Build or Buy software?
| Integration Questions | Build | Buy |
| Are you interested in rolling out the integration within a shorter time frame? | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Do you have in-house resources ready to prioritize the development, maintenance, and customization of the integration? | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Is your integration scope broad and complex, spanning multiple departments, teams, and companies? For instance, orchestrating complex workflows across 3 different companies with interdependent fields and data mappings. | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Are you an MSP or MSSP encountering higher integration requests from your partners or customers? | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Do you want a cost-effective integration in the long run? | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Do you want your business to drive the integration and not the other way around? | ❌ | ✔️ |

Frequently Asked Questions
Can Exalate handle integrations between more than two platforms simultaneously?
Yes. Exalate supports multi-platform integration scenarios, connecting three, four, or more systems in a single workflow. For example, you can sync Jira work items to ServiceNow incidents while also routing customer-reported items from Zendesk into Jira, with status updates flowing across all three platforms. Each connection is configured independently, so adding a new platform to your integration ecosystem doesn’t require redesigning existing connections.
How does AI-assisted configuration actually reduce setup time?
Aida generates working sync scripts from natural language prompts. Instead of learning Groovy scripting syntax, researching API documentation, and writing code from scratch, you describe what you want in plain language—”sync high-priority bugs from Jira to ServiceNow, include comments, update status bidirectionally”—and Aida produces the script. You review, test, and deploy. For complex integrations that traditionally took 20+ hours to configure, teams report setup times dropping by 50% or more.
What happens if one side of a cross-company integration goes down?
Exalate uses a transactional sync queue that tracks all changes in the order they occurred. If one side experiences downtime (say, your partner is upgrading their Jira instance), changes continue to queue on your side. When the other system comes back online, all queued changes sync in the correct sequence. No data is lost, and no manual intervention is required to restore synchronization order.
How does Exalate handle security for cross-company data exchange?
Each organization in a cross-company integration controls its own sync rules independently. You define what data you send and receive; the other party can’t override or access your settings. Authentication uses JWT tokens with automatic rotation, and all data moves over TLS 1.2/1.3 encryption. Exalate holds ISO 27001:2022 and SOC 2 Type II certifications. For organizations requiring maximum data control, on-premise and Docker deployment options are available. Full security details are available in the Exalate Trust Center.
Is Exalate suitable for organizations that need to connect legacy systems?
Exalate supports custom REST API connectors alongside its native connectors for platforms like Jira, ServiceNow, Salesforce, Azure DevOps, Zendesk, Freshservice, Freshdesk, GitHub, and Asana. If your legacy system exposes a REST API—even a basic one—Exalate can connect to it. This makes it practical for government agencies, manufacturing companies, and enterprises that need to bridge older systems with modern cloud platforms without replacing existing infrastructure.
How does the build vs. buy decision change for cross-company integrations?
Cross-company integration adds layers of complexity that heavily favor buying over building. You need independent control for each organization, secure data exchange without sharing system access, error handling that works across organizational boundaries, and resilience when either side changes its internal systems. Building all of this from scratch requires engineering not just the data sync, but the entire trust and access control framework, which is essentially what platforms like Exalate already provide.
What’s the typical ROI timeline for choosing a commercial integration solution over building custom?
Most organizations see positive ROI within the first quarter, driven by faster deployment (weeks vs. months), eliminated development costs, and reduced maintenance overhead. The gap widens over time as maintenance costs for custom builds compound annually (15–20% of original development cost per year) while commercial license costs remain predictable. Use the Exalate Pricing Calculator to model your specific scenario.
Can Exalate support hybrid integration strategies?
Absolutely! This is one of Exalate’s core strengths. You get a commercial platform with pre-built connectors and infrastructure for the heavy lifting, combined with a Groovy-based scripting engine for custom logic. You’re not locked into templates, and you’re not building from scratch. The scripting layer lets you implement conditional mappings, custom transformations, dynamic routing, and any business logic your use case requires, while Exalate handles connectivity, error management, security, and API change resilience underneath.
Recommended Reading:
- The Comprehensive Guide to iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service)
- B2B Integration: The Comprehensive Guide
- The Journey of Software Integration: How Organizations Make the Leap from Copying Data to Cross-Company Integration
- MSP Integration: Why It Matters for Your Business
- How Integration Service Providers Can Help Simplify Data Integration