Service desk integration connects two or more service desk platforms to synchronize tickets, share data, and create unified support workflows across teams and organizations.
In some cases, an organization might have more than one service desk application, which means they need to find a way to integrate all of them.
That’s where service desk integration comes in. You need a system connecting multiple service desks to create a unified, coherent ecosystem for managing and monitoring all support services.
Note: If you’re working with Jira, keep in mind that Jira now refers to “issues” as “work items.” Throughout this guide, we’ll use the updated terminology.
Key Takeaways
- Service desk integration synchronizes tickets, comments, attachments, and status updates between platforms to eliminate manual data entry and copy-paste workflows.
- Organizations integrate service desks to reduce administrative overhead by 25-40%, improve response times, enable cross-team collaboration, and gain unified reporting visibility.
- Evaluate integration platforms based on bidirectional sync capabilities, AI-assisted configuration, security certifications, supported connectors, and flexible mapping options.
- Real-world applications span support-to-development escalation, MSP multi-client management, cross-departmental workflows, vendor collaboration, and global service desk consolidation.
- Successful integration requires clear planning, phased rollouts, thorough testing, continuous monitoring, and investment in user training.

What Is Service Desk Integration?
Service desk integration is the process of unifying and consolidating data from two or more service desks to establish a seamless, coherent service ecosystem.
Here is a typical service desk integration scenario:
The support team uses Zendesk or Freshdesk to gather information about incidents or tickets reported by users, while the IT team uses Jira to resolve tickets that require the dev team’s attention.
In this scenario, the manager or admin has to integrate both Zendesk and Jira in order to streamline the efforts of both teams and ensure smooth collaboration.
What Are the Main Types of Service Desk Integration?
Service desk integration comes in multiple forms, each designed to solve specific business challenges. Similar to ITSM integration, service desk integration occurs in various forms:
- System Integration synchronizes service desk platforms to enable seamless workflows between internal teams or external partners. When your L1 support team in Zendesk escalates a ticket to your development team in Jira, system integration ensures the ticket, its complete history, comments, and attachments flow between both platforms in real-time.
- Data Integration helps customer success managers pull ticket information from platforms like Zendesk, Freshdesk, Freshservice, and Jira Service Management into a unified reporting layer.
- Point-to-Point Integration uses APIs or webhooks to establish a dedicated communication channel between exactly two tools. This works for simple scenarios but becomes unmanageable as you add more platforms.
- Hub-and-Spoke Integration uses a central integration hub that connects all service desks through a single intermediary platform, instead of creating individual connections between every system pair. This reduces the number of connections needed from n(n-1)/2 to just n.
- Legacy System Integration connects modern service desks with older, on-premise ITSM platforms that may lack modern APIs or cloud connectivity. Organizations running Azure DevOps Server or other on-premise tools often need this approach.
- Middleware-Based Integration uses dedicated integration platforms (iPaaS solutions) that sit between service desks and handle all data transformation, routing, and orchestration logic. These platforms abstract away the complexity of dealing with different APIs and data formats.
- Self-Service Portal Integration connects knowledge bases and user portals with your service desk infrastructure to empower users to resolve common issues independently.
- Vendor Integration establishes connections between your organization’s service desk and external managed service providers, software vendors, or third-party support teams.
- Hybrid Integration bridges cloud-based service desks with on-premise systems, a common scenario during cloud migration projects or for organizations with mixed infrastructure.
What’s the Difference Between ITSM and Service Desk?
A common misconception is that ITSM (IT service management) and service desk are interchangeable concepts. Despite their similarities, some key factors differentiate them.
ITSM is a framework of practices and procedures governing the entire spectrum of IT services. It covers everything from detection to delivery, ensuring that the business requirements stay at the forefront.
Platforms like Zendesk, Freshdesk, Freshservice, ServiceDesk Plus, Asana, and Jira Service Management can be used as service desks.
A service desk is only one aspect of ITSM, which focuses on handling technical issues for customers. It serves as a portal where users file service requests and get timely assistance.
The service desk has a smaller catchment area compared to the ITSM framework—a service desk is a sub-category of ITSM. While a service desk handles support services, ITSM focuses on managing the entire scope of service delivery.
| ASPECT | SERVICE DESK | ITSM |
| Scope | Single point of contact for IT support | Complete IT service lifecycle framework |
| Primary Focus | Incident resolution, service requests, customer support | Strategy, planning, delivery, and continuous improvement |
| Activities | Ticket management, L1/L2 support, work item escalation | Change management, asset management, problem management, SLA governance |
| Users | End users, employees, customers | IT teams, business stakeholders, executives |
| Tools | Zendesk, Freshdesk, Freshservice, ServiceNow Service Portal | ServiceNow ITSM Suite, BMC Remedy, Jira Service Management |
| Metrics | First response time, resolution time, CSAT scores | Business alignment, service availability, cost per service |
| Relationship | Component of ITSM | Framework containing service desks |
Why Should Organizations Integrate Service Desks?
There are many reasons why businesses choose to integrate their service desks. Here are the core benefits:
To Create a Unified View of Support Operations
In companies where independent teams provide assistance to customers, integrating service desks helps consolidate their efforts into a single hub.
This makes it easier for agents to stay on the same page when assisting customers and tracking incidents. Support managers no longer have to toggle between three different platforms to understand what’s happening across their teams.
This consolidation means faster ticket location, consistent responses regardless of which system received the request, and executives who can see complete support metrics without manual data compilation.
To Improve Operational Efficiency
Service desk integration lets companies automate processes such as ticket prioritization and routing through a unified platform. This decreases the time needed for sorting and responding to incidents, which also improves the average response time.
Automated ticket routing sends work items directly to the right team based on keywords, priority levels, or customer segments, eliminating the 30-45 minutes agents spend daily deciding where tickets belong.
When your Zendesk support team escalates to your development team on Jira, the ticket transfers instantly with full context instead of requiring someone to manually copy information between platforms.
To Foster Collaboration
Service desk integration gives agents and admins a unified view. This makes collaboration easier since everybody has access to the same data sets.
As a result, managers and support agents from different teams can share information seamlessly, fostering a collaborative work environment. Support agents in Freshdesk can see updates from developers working in Jira without sending status-check emails.
For organizations with external partners or MSPs, integration enables vendors to see exactly what they need to resolve work items while your sensitive internal data stays protected within your system.
To Improve the User Experience
Integrating service desks provides a better user experience for customers (end users) and employees alike.
In the scenario mentioned earlier, employees enjoy better access to real-time information, which helps them address incidents and change requests better. Similarly, the improved employee experience trickles down to the end users.
When the agent has a better understanding of the incident as well as up-to-date information, they can provide better, detailed assistance to the customer.
End users don’t care which service desk receives their reques; they just want fast, accurate help.
To Improve Data-Oriented Services
When it comes to analysis and reporting, integrating multiple service desks is the best approach.
Unifying data makes it possible to consolidate everything into one view, from which you can obtain updates, generate reports, and analyze performance. This gives you the insights needed to optimize operations to improve efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Service desk integration also eliminates duplicate tickets, inconsistent data entry, and reporting gaps. You can analyze patterns across all your service desks, not five separate reports that you manually combine in spreadsheets.
To Reduce Operational Costs
Manual processes cost money. Every minute agents spend copying tickets between systems, searching for information across platforms, or waiting for updates from other teams adds to your support costs.
Integrating your service desks reduces the time spent on administrative tasks by 25-40%. It also reduces ticket volume by deflecting 30-50% of routine requests, letting your team focus on complex work items that truly need human expertise.
For MSPs, integration means one standardized process serves multiple clients instead of maintaining separate workflows for each customer.

Calculate time and money savings from automated bidirectional sync.
To Enable Proactive Problem Management
Integrated service desks reveal patterns invisible in siloed systems. When three customers report similar problems across different platforms, integration connects these dots and flags the pattern for your problem management team.
You can identify root causes faster and implement permanent fixes instead of repeatedly addressing symptoms. Integrating monitoring tools also helps your team catch problems before users notice them.
To Support Scalability for Growing Organizations
As organizations grow, they acquire new tools, onboard new teams, and expand into new markets. Service desk integration provides the flexibility to add systems without rebuilding your entire support infrastructure.
When you acquire a company using a different service desk, integration lets both platforms coexist while sharing necessary information.
For organizations expanding internationally, integration connects regional service desks using local languages and currencies while maintaining oversight across all regions.
Service Desk Integration Tools
When you want to integrate two or more service desks without compromising security and process efficiency, here are some tools to consider:
Zapier
Zapier is a workflow automation platform that allows users to connect multiple service desks, CRMs, ERPs, and applications using Zaps.
When you create Zaps between two service desks, you can configure triggers to control what gets sent and when it leaves.
Limited for complex enterprise scenarios requiring bidirectional sync or custom field transformations.
Workato
Workato is an enterprise automation solution that allows users to connect enterprise applications. You can configure connections using Workato recipes, a set of instructions that controls the automation of complex workflows.
With Workato, users can integrate service desks for access to both simple and complex features, from detecting the tone of the ticket to creating bots using AI and machine learning.
Best for: Large enterprises with dedicated integration teams who can invest in building and maintaining complex recipes.
Exalate
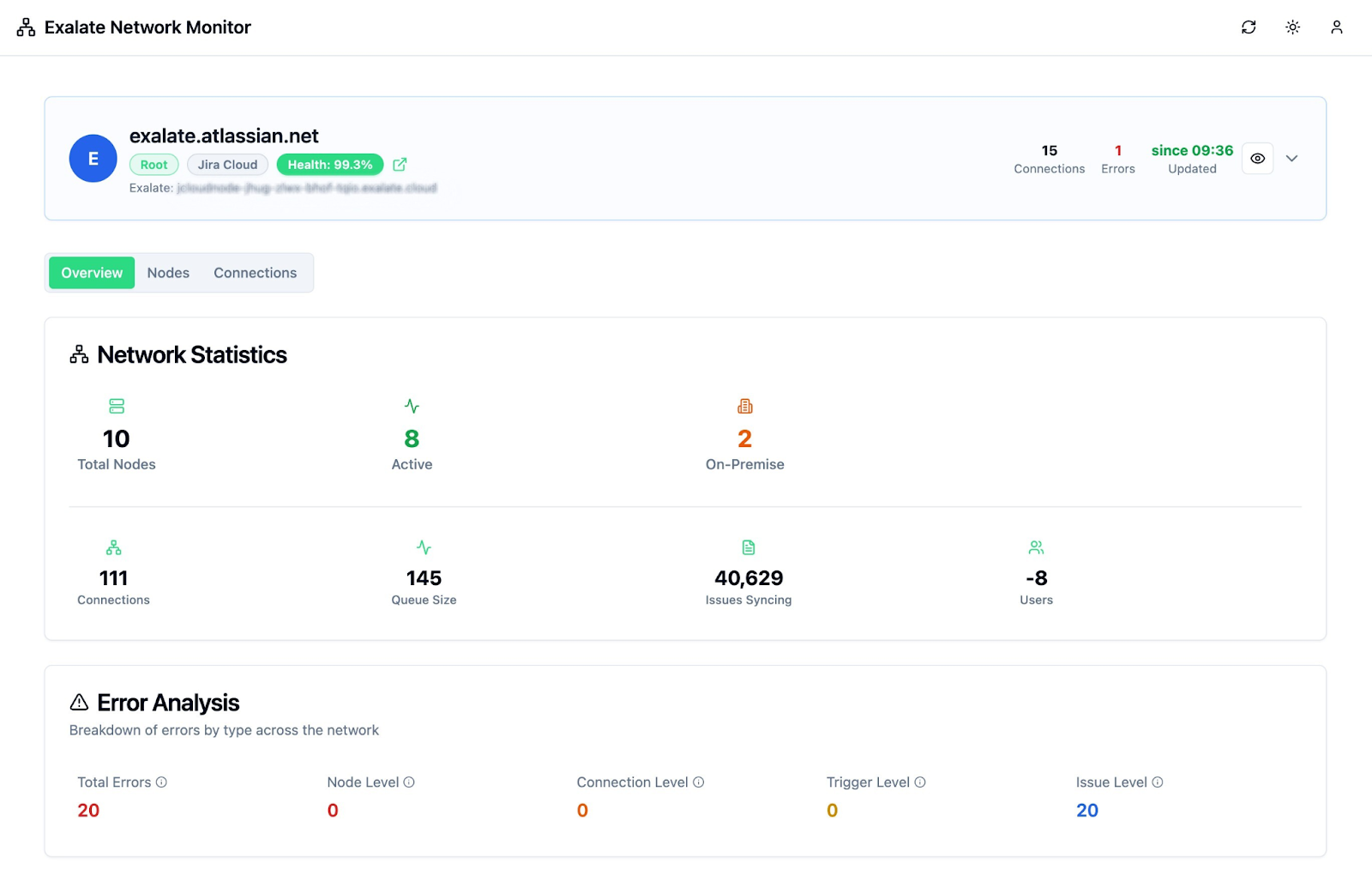
Exalate is an iPaaS solution designed for bidirectional synchronization between service desk platforms. Supported platforms include Jira (Cloud and Service Management), Zendesk, Freshdesk, Freshservice, ServiceDesk Plus, ServiceNow, Salesforce, Azure DevOps, Azure DevOps Server, Asana, GitHub, and custom connectors for proprietary systems.
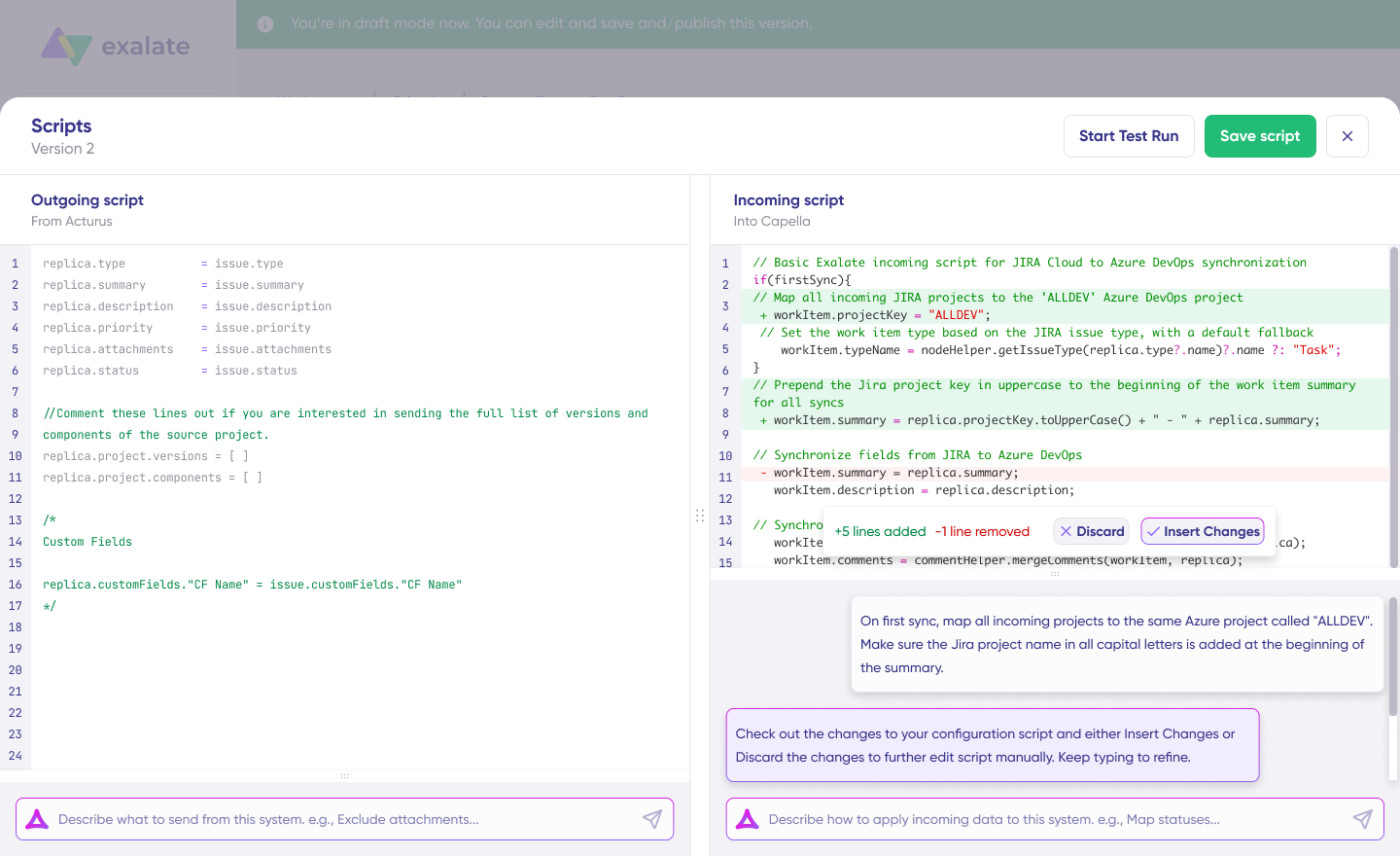
Exalate offers AI-powered configuration through two tools: Aida is a scripting co-pilot that generates synchronization configurations from natural language descriptions. So you can describe “sync all high-priority tickets from Zendesk to Jira with matching status values” and get a working configuration without writing code.
Each side of an Exalate connection maintains independent control over its own instance. This means only your admins can make changes to your side of the connection, making it ideal for MSPs and cross-company integrations where data sovereignty matters. Security details are available at the Trust Center.
Best for: Organizations needing bidirectional sync, cross-company collaboration, or complex field mappings without deep scripting expertise.

Jitterbit
Jitterbit is an iPaaS solution that allows users to connect systems and build applications. It works well for advanced IT teams looking to work with custom systems.
Jitterbit Harmony is the low-code integration platform that allows you to automate workflows and streamline business processes across enterprise applications, legacy systems, and cloud services.
Best for: Organizations with custom or legacy systems requiring significant API development work.
Microsoft Power Automate
Microsoft Power Automate is an integration solution that enables users to integrate service desks for sharing data and analyzing incidents in real time. Thanks to its database of Actions and Flows, Power Automate allows users to automate workflows and improve service experience.
With Power Automate, you can access a library of pre-built connectors for connecting apps, service desks, CRM platforms, and ERPs. The AI Builder allows users to create intelligent automation and find insights using tailored AI models.
Best for: Organizations already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem who need simple workflow automation between Microsoft-friendly applications.
Common Service Desk Integration Challenges (and How to Solve Them)
Here are the most common challenges and practical solutions to overcome them.
Data Mapping Inconsistencies
Different service desk platforms use different field names, data types, and values for the same information. Zendesk uses priority values like “Urgent, High, Normal, Low” while Jira uses “Highest, High, Medium, Low, Lowest.” Custom fields create even more complexity; a specific field in ServiceNow might not exist in Freshdesk at all.
The Solution: Create a data mapping document that defines how fields translate between platforms before starting integration. Use integration tools with transformation capabilities to convert values automatically, mapping Zendesk’s “Urgent” to Jira’s “Highest” without manual intervention.
For fields that don’t have direct equivalents, decide whether to create custom fields in the target platform, store the data in description/comment fields, or exclude it from synchronization. Tools like Exalate handle these mappings automatically once configured.
Security and Data Privacy Concerns
Integrating service desks means data flows between systems, potentially crossing organizational boundaries when working with MSPs or vendors. Organizations worry about exposing sensitive customer information, violating compliance requirements like GDPR, or giving external partners access to internal data they shouldn’t see.
The Solution: Choose integration platforms with granular filtering and independent control for each side of the connection. Configure field-level permissions that sync only necessary information. External vendors might see ticket summaries and status updates, but not customer email addresses or payment information.
Use data masking for sensitive fields like phone numbers or account IDs when syncing to external systems. Most importantly, select integration solutions where each organization controls what leaves their environment.
Mismatched Workflows and Business Processes
Each service desk platform reflects the unique workflows of the teams using it. Your support team’s five-stage ticket lifecycle in Zendesk doesn’t match your development team’s eight-stage process in Jira. When tickets sync between systems with mismatched workflows, status updates become confusing, and automation breaks down.
The Solution: Map workflows between platforms by identifying equivalent stages > Zendesk’s “Open” might correspond to Jira’s “To Do” while “Pending” maps to “In Progress.”
Use status translation rules in your integration to convert values automatically. For workflows that truly don’t align, consider creating intermediate statuses or using a common subset of stages that both platforms share.
Performance and Sync Latency
Large organizations process thousands of tickets daily. When integration performance lags, tickets take minutes or hours to appear in the target system, creating confusion when agents don’t see recent updates. Sync failures accumulate, creating backlogs that require manual intervention to resolve.
The Solution: Choose integration platforms designed for high-volume scenarios with asynchronous processing and queue management. Implement selective syncing that transfers only tickets meeting specific criteria rather than syncing everything; you might sync only high-priority tickets or those tagged for specific teams.
Use webhook-based integrations for real-time updates instead of polling-based approaches that check for changes on fixed schedules. Monitor integration performance regularly and scale infrastructure as ticket volumes grow.
Lack of Technical Resources and Expertise
Many organizations lack in-house integration expertise. Building and maintaining custom API integrations requires developers who understand both platforms, authentication methods, error handling, and ongoing maintenance. Small IT teams can’t dedicate resources to writing and troubleshooting integration code.
The Solution: Use platforms that provide AI-assisted configuration instead of requiring custom development. Exalate’s Aida generates integration logic from natural language descriptions, so you describe what you need rather than coding it.
Start with pre-built integration templates provided by iPaaS vendors rather than building from scratch. Invest in training programs for existing IT staff on integration platforms to build internal capabilities over time.
Legacy System Compatibility
Older on-premise service desks lack modern REST APIs. These legacy systems use outdated protocols, require direct database access, or have limited customization options that prevent standard integration approaches.
The Solution: Use enterprise integration platforms with legacy connectors specifically designed for older ITSM systems. Consider middleware that can translate between modern APIs and legacy protocols like SOAP or direct database connections.
For systems without any API access, evaluate screen-scraping tools or robotic process automation (RPA) as a temporary bridge. Plan a phased migration strategy that uses integration to transition from legacy systems to modern platforms gradually.
Integration Maintenance Over Time
Service desk platforms release updates that change APIs, deprecate features, or modify data structures. An integration working perfectly today breaks after a vendor updates their platform. Organizations discover integration failures weeks later when accumulated sync errors create visible problems.
The Solution: Choose integration platforms that handle vendor API changes automatically rather than requiring manual updates to custom code. Set up monitoring and alerting that immediately notifies administrators when sync failures occur.
Test integrations in sandbox environments after major platform updates before they affect production. Build error handling into your integration logic that logs failures and retries automatically rather than silently dropping data.
Cost Justification and ROI Concerns
Integration projects require upfront investment in software licenses, implementation time, and ongoing maintenance. Executives question whether integration costs justify the benefits, especially when teams have managed with manual processes for years.
The Solution: Calculate current costs of manual ticket handling—hours spent copying information between systems, delays caused by handoff friction, and duplicate work across teams.
Document time savings from automation, showing that eliminating 30 minutes of manual work per agent daily translates to substantial annual cost savings. Track metrics before and after integration, like average resolution time, first-response time, and customer satisfaction scores, to demonstrate tangible improvements.

Calculate time and money savings from automated bidirectional sync.
Service Desk Integration Use Cases
Here are proven use cases showing how organizations connect platforms like Jira, Zendesk, Freshdesk, Jira Service Management, ServiceNow, Freshservice, Asana, and ServiceDesk Plus.
Connecting Customer Support with Development Teams
Case: Support teams typically use platforms like Zendesk, Freshdesk, or Freshservice to manage customer inquiries, while development teams work in Jira to track bugs and feature requests. Manual escalation creates delays and context loss.
Solution: Bidirectional sync automatically creates a Jira work item when a Zendesk ticket requires development attention. All relevant context—ticket summary, description, customer priority, affected product version, and attachments—flows with the ticket. As developers update the Jira work item with progress notes or resolution details, those updates flow back to Zendesk so support agents can keep customers informed without switching platforms.
MSP Service Desk Management
Case: Managed Service Providers face unique challenges managing support operations across dozens or hundreds of client organizations. Some clients use ServiceNow, while others prefer Freshservice or ServiceDesk Plus, while the MSP maintains its internal operations in Jira Service Management.
Solution: Create separate integrations for each client while maintaining complete data isolation. The MSP’s Jira Service Management instance connects to each client’s service desk through individual connections. When a client reports a work item in their ServiceNow instance, a corresponding ticket is created in the MSP’s Jira Service Management with appropriate context about which client it belongs to, the service level agreement terms, and escalation requirements.
Internal IT Service Management Across Departments
Case: Large enterprises often run multiple service desk instances across different departments. The IT department might use Jira Service Management for infrastructure requests, HR uses Freshservice for employee onboarding, and facilities management operates ServiceDesk Plus for building maintenance. When work items require cross-departmental coordination—like onboarding a new employee, which involves IT equipment, HR paperwork, and office space—information needs to flow between these isolated systems.
Solution: Integration connects departmental service desks so related requests stay linked. As each department completes its portion of the onboarding process, status updates sync across all platforms so coordinators see the complete picture.
Multi-Region Service Desk Consolidation
Case: Global organizations often operate regional service desks in different markets, each using platforms suited to local requirements. European operations might use ServiceNow for GDPR compliance features, Asian operations prefer Freshservice for regional language support, and North American teams work in Jira Service Management. Executive leadership needs consolidated visibility across all regions while allowing each to operate with appropriate local tools.
Solution: Each regional service desk continues operating independently while syncing aggregated data to a central reporting instance. Regional teams maintain autonomy over their workflows, data models, and user interfaces, but standardized information flows to headquarters for enterprise-wide analytics and resource allocation decisions.
A logistics company with operations in multiple countries implemented this pattern. Each region maintains its preferred service desk platform. They sync standardized fields, including incident category taxonomy, severity levels, affected business units, and customer satisfaction scores.
Change Management and Incident Coordination
Case: When planned changes cause incidents, or when recurring incidents reveal the need for infrastructure changes, information must flow between change records in ServiceNow or Jira Service Management and incident tickets in various service desk platforms.
Solution: Integration automatically links related incidents and changes across platforms. When a scheduled maintenance window in ServiceNow connects to a system deployment tracked in Jira, any incidents reported during that window link back to the originating change.
This provides change managers with immediate feedback about change impacts and helps incident responders understand that a spike in database connection errors correlates with a database version upgrade, helping teams troubleshoot faster.
Project Management and Service Desk Alignment
Case: Product teams using Asana for project management need visibility into support tickets affecting their products. Support teams need to flag feature requests and bugs to product teams without manual ticket recreation.
Solution: Sync relevant tickets from Freshdesk or Zendesk to Asana tasks when they meet specific criteria, like being tagged as “feature-request” or “product-bug.” Product managers see incoming feedback in their existing workflow without monitoring the support queue.
Best Practices for Service Desk Integration
For any service desk integration effort to succeed, here are the practices that separate successful implementations from troubled ones.
Always Work With a Plan
Before implementing service desk integration, establish a strategy that aligns with your needs and prospects. You need a clear understanding of what you want to achieve with the integration and how it ties into your organizational requirements.
Your integration plan must account for timelines, deliverables, milestones, responsibilities, and expectations. Factor in the tools needed for gathering data and sharing updates. Define success criteria upfront, whether that’s reducing ticket handoff time by 50%, eliminating duplicate tickets, or improving customer satisfaction scores.
Embrace Automation and AI
Automation is the core value proposition of service desk integration. Consider using automated integration solutions to reduce bottlenecks in manual processes. By thoroughly assessing your existing service desk processes, tools, and data, you can spot potential areas for improvement.
Look for tools with AI-powered assistants. Exalate’s Aida generates synchronization configurations from natural language prompts, reducing the technical barrier to complex integrations.
Track Progress and Key Metrics
After integrating data from different service desks, monitor key metrics to know when to make changes. This determines whether the integration solution is the right fit for your organization.
Track metrics like ticket sync success rate, average sync latency, reduction in manual handoff time, impact on resolution time, and customer satisfaction changes. Use accurate reporting tools to monitor the progress and quality of responses to incident requests.
Document Integration Configuration Thoroughly
Integration configurations become complex quickly, especially when implementing custom transformation logic. Maintain comprehensive documentation that explains your field mappings, sync triggers, conditional logic, and transformation rules.
Document not just what the integration does but why; explain the business reasoning behind decisions like “we sync only public comments to external systems because internal notes contain strategic information.”
Create procedures for scenarios like “what to do when tickets stop syncing,” “how to manually trigger sync for stuck tickets,” or “process for adding new custom fields to existing integrations.”
Invest in User Training and Change Management
Conduct hands-on training sessions that show agents exactly how to escalate tickets, where to find updates from other teams, and what they need to do differently now that systems are connected.
Create quick reference guides with screenshots showing integrated workflows—”How to escalate a Zendesk ticket to Jira development.”
Designate integration champions within each team who receive advanced training and can answer colleagues’ questions. Gather feedback continuously from users about friction points, missing data, or workflow improvements.
Use Secure Integration Tools
Always prioritize security when choosing a service desk integration solution. You want to keep your customer data safe from unauthorized access.
When integrating with another company, ensure that the tool grants each side independent control over its own data. Look for platforms with ISO certification and transparent security practices documented in a trust center.
Plan for Phased Rollouts
Avoid the temptation to integrate everything at once. Start with a single, well-defined use case, perhaps syncing high-priority tickets between support and development. Once that integration runs smoothly, expand to additional scenarios.
This approach lets you identify issues early, build organizational confidence, and refine your processes before scaling to more complex integrations.

FAQs
What’s the difference between ITSM and a service desk?
A service desk is a single component within ITSM (IT Service Management). ITSM is the complete framework for managing all IT services across an organization, covering strategy, planning, delivery, and continuous improvement. The service desk specifically handles incident resolution, service requests, and user support within that broader framework.
How does Exalate differ from other integration tools?
Exalate gives each organization independent control over its own instance and what data leaves its environment. This is ideal for MSPs, regulated industries, and cross-company collaboration where data sovereignty matters. Exalate also provides AI-powered configuration through Aida (scripting co-pilot) to reduce technical barriers.
What fields and data can Exalate sync between service desks?
Exalate syncs standard fields like ticket summary, description, status, priority, assignee, reporter, comments, attachments, labels, due dates, and SLA timers. It also handles custom fields specific to your organization: customer tier, product version, escalation codes, internal reference numbers, or any custom data structures. You can apply conditional logic, data transformations, and filtering rules to control exactly what syncs and how it’s formatted in each platform.
Can Exalate integrate with on-premise service desk systems?
Yes, Exalate supports both cloud and on-premise service desk platforms. It integrates with on-premise systems like Azure DevOps Server, ServiceNow on-premise instances, and ServiceDesk Plus on-premise deployments. Exalate’s flexible architecture handles REST APIs, SOAP protocols, and various authentication methods.
What security measures does Exalate provide?
Exalate maintains ISO 27001:2022 certification and provides granular field-level filtering, data masking, encrypted connections, and role-based access controls. Each organization runs its own instance with independent control over what data leaves its system. Find detailed security documentation at the Trust Center.
Can Exalate support MSPs with multiple clients?
Yes, Exalate is well-suited for MSPs. Each client connection runs independently, so API changes or configuration updates for one client don’t affect others. MSPs can use proven integration templates across clients while maintaining each client’s unique field mappings and security requirements.
What platforms does Exalate support for service desk integration?
Exalate supports Jira Cloud, Jira Service Management, ServiceNow, Zendesk, Freshdesk, Freshservice, Salesforce Service Cloud, Azure DevOps, Azure DevOps Server, Asana, GitHub, ServiceDesk Plus, and custom connectors for proprietary systems. Check the integrations page for the current list.
How does AI-assisted configuration work in Exalate?
Aida is a scripting co-pilot that generates synchronization configurations from natural language descriptions. So you describe what you need (like “sync high-priority tickets from Zendesk to Jira with matching status values”) and get a working configuration without writing code.
If you’re considering service desk integration and have questions, book a session to discuss them with an integration engineer.
Recommended Reading:
- The Complete Blueprint for Aligning Your Service Desk and Development Teams (Process Integration and Best Practices)
- ITSM Integration: Simplify Your IT Services Like Never Before
- An Overview of Integrated Service Management (ISM)
- Integration as a Service (IaaS): Everything Explained
- B2B Integration: The Comprehensive Guide
- Zendesk Integrations: Streamline Teams Working in Zendesk and Other Tools